Case Author(s): Eric Hutchins, M.D. and Keith Fischer, M.D. , 08/09/05 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Bilateral Cortical Necrosis
Brief history:
2 day old oliguric boy whose delivery was complicated by placental abruption.
Images:
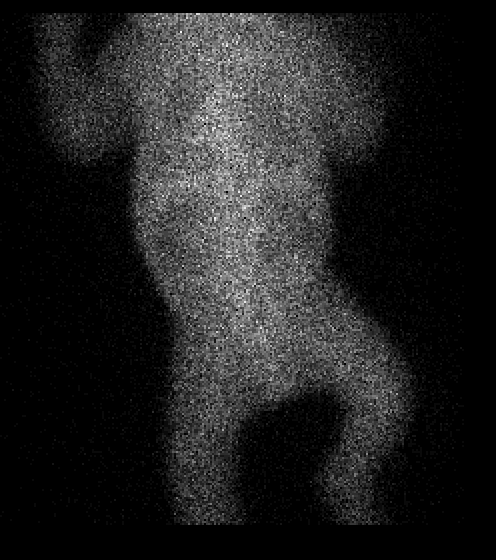
Posterior image 20 minutes after injection of radiopharmaceutical. You can also view the 20-minute acquisition as an AVI image.
View main image(rs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(rs).
Sample sequential 20 second posterior images from the initial 20 minutes of imaging.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Bilateral Cortical Necrosis
Full history:
2 day old male with oliguria presents for evaluation of renal perfusion and function. His delivery was complicated by placental abruption. Renal scintigraphy was requested for further evaluation.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Tc-99m MAG3
Findings:
No identifiable renal perfusion was demonstrated on the radionuclide angiogram or on sequential renal images extending to 20 minutes.
Discussion:
The etiologies of acute renal failure in a newborn are divided into prerenal, intrinsic renal, and obstructive catagories.
Cortical necrosis may be associated with hypoxic insults such as perinatal anoxia, placental abruption, twin-twin transfusion, or twin-maternal transfusion.
Absence of perfusion to the kidneys in a neonate could be due to cortical necrosis, bilateral renal vein thrombosis, or (less likely) bilateral renal artery thrombosis.
Reference:
Andreoli SP, "Acute Renal Failure in the Newborn" Semin Perinatol. 2004 Apr;28(2):112-23.
Differential Diagnosis List
Cortical necrosis, renal artery thrombosis, renal vein thrombosis
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Renal Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Genitourinary System, Category:Other generalized systemic disorder)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: rs035
Copyright by Wash U MO

