Case Author(s): Thomas H. Vreeland, M.D., Tom R. Miller, M.D., Ph.D., Jerold W. Wallis, M.D., Henry D. Royal, M.D. , 7/21/94 . Rating: #D2, #Q5
Diagnosis: Renal Artery Stenosis
Brief history:
This is a 60 year-old man with hypertension undergoing evaluation for renal artery stenosis.
Images:
View main image(rs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(rs).
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Renal Artery Stenosis
Full history:
This is a 60 year-old physician otherwise in good health who experienced sudden onset of hypertension.
Findings:
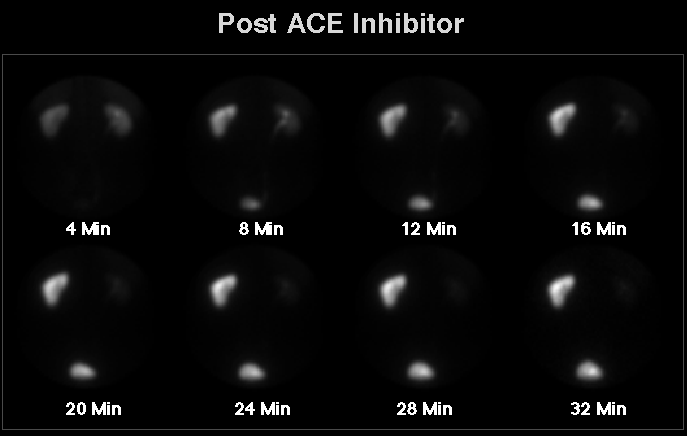
For the first study the patient was given 2.5 mg enalapril intravenously over a five minute period followed by administration of Tc-99m MAG3. There is marked asymmetry in function, with normal uptake and excretion by the right kidney (on the viewer's right), but significant retention of radiopharmaceutical by the left kidney with little or no excretion. Based on
initial uptake of tracer, relative split function was equal, with 49% on the right and 51% on the left.
The second study, performed without administration of enalapril, shows dramatically improved left renal function.
Uptake and excretion are only minimally delayed on the left.
Discussion:
Renal scintigraphy with angiotensin converting enzyme
inhibitors is a sensitive and specific way to screen
patients with suspected renovascular hypertension.
Either the rapid-onset intravenous ACE inhibitor enalapril,
or the slower-acting oral captopril agent may be used.
Enalapril is probably preferable because of its faster
and more reproducible effect. If the initial study
performed with the ACE inhibitor is normal, some
practicioners will not do the baseline study. If the
initial study is abnormal, as in the present case, it
is essential that the baseline examination be performed to evaluate the possibility of unilateral, non-renovascular renal disease.
Followup:
After the renal scinitgraphy an arteriogram was performed showing a high-grade left renal artery lesion just distal to the ostium with only minimal disease on the right. The left renal artery lesion was treated by balloon angioplasty with only a minimal residual stenosis. The blood pressure promptly returned to a level close to normal.
View followup image(an).
Major teaching point(s):
Renal scintigraphy with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors is an accurate non-invasive way to screen patients for renovascualr hypertension.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
- General ACR code: 87
- Genitourinary System:
8.1217 "Nuclear medicine study-genitourinary"8.12174 "Renal imaging with pharmacologic intervention include: imaging with use of diuretics, or with angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors"
8.124 "Angiography (see also 9.)"
8.1243 "Selective renal angiography"
8.4557 "Renal artery stenosis"
References and General Discussion of Renal Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Genitourinary System, Category:Organ specific)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: rs001
Copyright by Wash U MO

