Case Author(s): Xia Wang, M.D., Tom R. Miller, M.D., Ph.D. and Barry A. Siegel, M.D. , 09/02/05 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Pulmonary Metastases from Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma.
Brief history:
57-year old man with a history of follicular thyroid cancer, a negative whole body I-131 scan, and an elevated serum thyroglobulin.
Images:
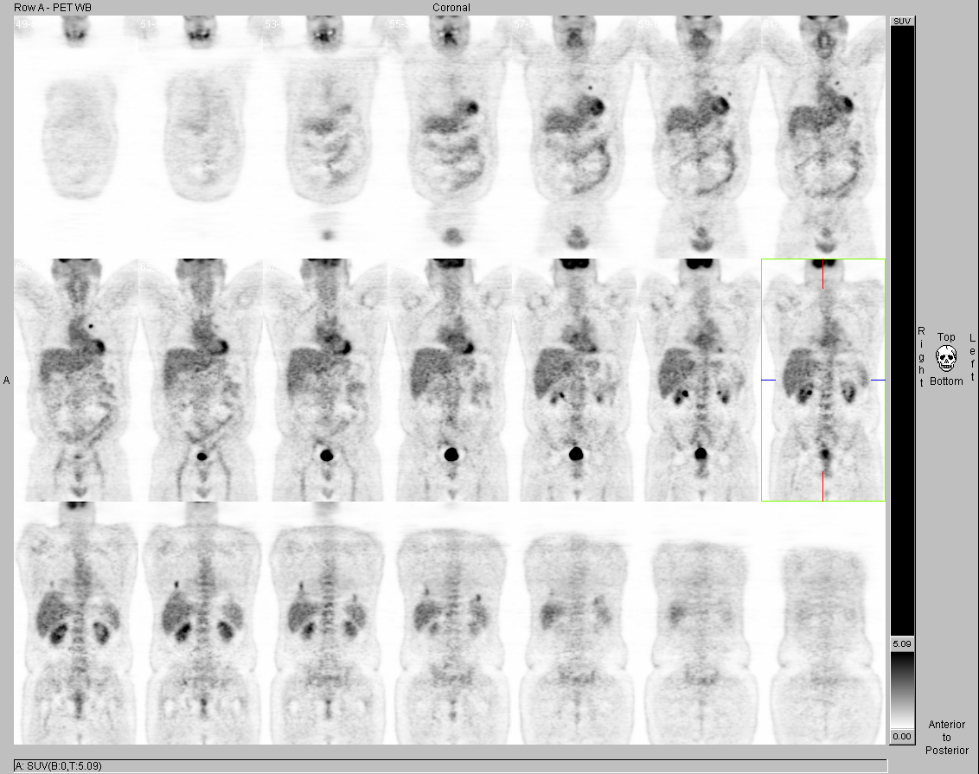
Coronal FDG-PET images. View MIP cine in AVI format.
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Axial PET/CT images of the chest
View third image(pt).
Axial PET/CT images of the chest
View fourth image(mc).
Anterior and posterior I-131 whole-body images
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Pulmonary Metastases from Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma.
Full history:
57-year-old man with follicular thyroid carcinoma diagnosed in 1989, status post complete thyroidectomy in 09/1989 followed by treatment with 100 mCi of I-131 on 12/9/89. The patient now presents with an elevated serum thyroglobulin of 29 ng/mL on 8/26/05. Whole-body I-131 imaging on 8/26/05 was negative for local recurrence or distant metastases. PET/CT is requested for restaging.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Radiopharmaceutical: 14.3 mCi F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose i.v. on 09/02/05.
5.2 mCi I-131 sodium iodide p.o. on 08/26/05
Findings:
PET/CT (09/02/05): There are multiple subcentimeter pulmonary nodules scattered throughout both lungs. At least seven nodules are FDG avid. The remainder of the nodules are too small to characterize on PET.
Whole-body I-131 images: There is no functioning thyroid tissue identified.
Discussion:
Whole-body I-131 imaging is the conventional method to detect residual or recurrent thyroid cancer after total thyroidectomy and I-131 ablation of any remaining thyroid tissue. Follicular thyroid carcinoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma, and mixed papillary-follicular carcinomas can concentrate radioiodine and can be demonstrated scintigraphically. Medullary carcinomas and anaplastic carcinomas do not concentrate radioiodine and are not detected with conventional I-131 scintigraphy. Although I-131 scanning has a very high specificity of 99%–100%, the frequency of I-131 positivity with recurrent disease is 50%–60% in patients with papillary carcinoma and about 65% in patients with follicular carcinoma. Most patients with thyroid cancer who present with I-131 accumulating metastases receive I-131 treatment, which may be curative.
Patients with elevated serum thyroglobulin levels and negative I-131 scans present both diagnostic and therapeutic dilemmas. Because progression in differentiated thyroid cancer occurs very slowly, patients have a relatively good prognosis and may live for many years even after metastatic disease has been detected, provided adequate treatment has been offered. However, patients with metastatic disease and negative I-131 scans are usually not treated with high-dose radioiodine. Thus, I-131 negative metastases need to be removed surgically, provided they can be localized. FDG-PET shows metastatic disease in up to 90% of these patients. Consequently, FDG-PET is a valuable diagnostic tool in patients with thyroid cancer who present with elevated serum thyroglobulin levels and negative I-131 imaging because it permits selection of patients for surgery, which also may be curative. FDG-PET is most likely to be positive with serum thyroglobulin levels >10 ng/L.
Reference:
Schluter B, Bohuslavizki KH, Beyer W, Plotkin M, Buchert R, Clausen M. Impact of FDG PET on patients with differentiated thyroid cancer who present with elevated thyroglobulin and negative 131I scan. J Nucl Med 2001; 42:71-6.
Macapinlac HA. FDG-PET in head and neck, and thyroid caner. Chang Gung Med J 2005; 28:284-295
Major teaching point(s):
In patients with differentiated thyroid cancer of follicular cell origin who present with elevated serum thyroglobulin levels and negative I-131 scintigraphy, FDG PET/CT is the modality of choice to detect local recurrences or distance metastasis.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Lung, Mediastinum, and Pleura, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt143
Copyright by Wash U MO

