Case Author(s): Xia Wang, M.D., Daniel Wessell, M.D., Ph.D., and Barry A. Siegel, M.D. , 08/01/05 . Rating: #D3, #Q4
Diagnosis: Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia
Brief history:
90-year-old woman with prolonged leukocytosis, anemia, and splenomegaly.
Images:
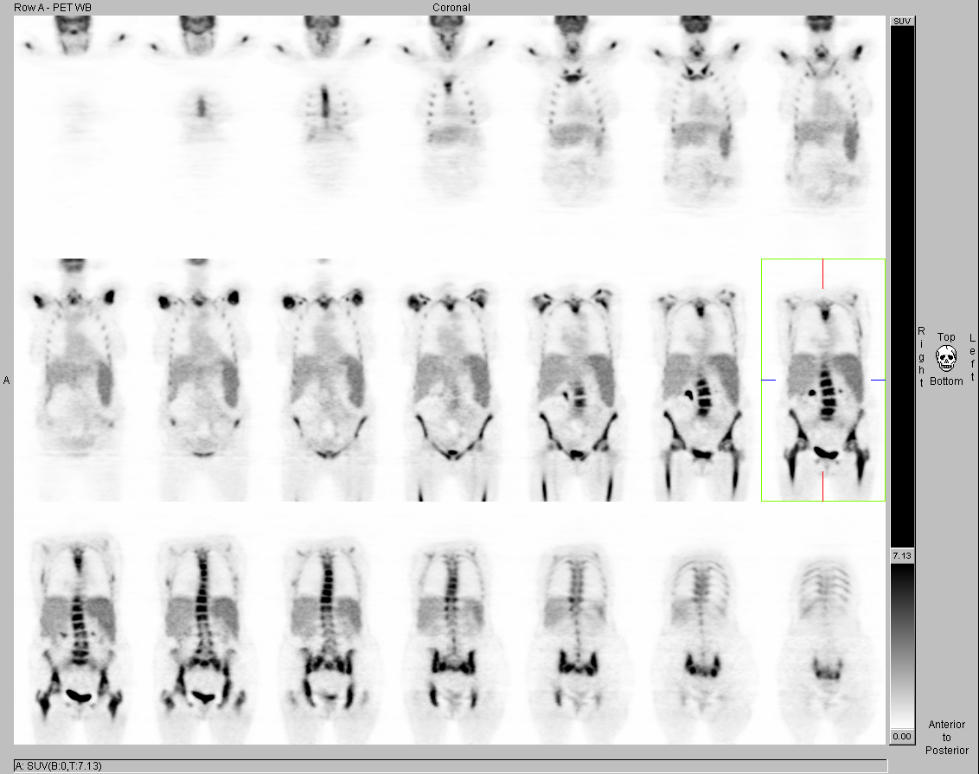
Coronal FDG-PET images. View MIP cine in AVI format.
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image().
CT image
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia
Full history:
90-year-old woman with prolonged leukocytosis, anemia, and splenomegaly. Multiple small low-attenuation lesions seen were within the spleen on recent CT and MRI of 07/23/05. PET/CT study was requested for diagnosis of possible lymphoma.
Findings:
PET/CT: There is markedly increased bone marrow uptake of FDG seen throughout the entire axial and the visualized appendicular skeleton, including the calvarium, with a maximum standardized uptake value(SUV) of approximately 11.0 within the vertebral bodies. Additionaly, there is mildly, diffusely increased FDG uptake within the spleen, with no focal lesions seen within the spleen on this study.
CT of abdomen: Splenomegaly with innumerable small hypoattenuating splenic lesions, is suggestive of spleen involvement, which is often seen in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. Infection is another possible explanation.
Discussion:
Diffusely increased FDG uptake in the bone marrow is commonly seen in patients with marrow hyperplasia as a result of hemolytic or iron-deficiency and blood-loss anemia. It is also commonly seen in patients who are undergoing chemotherapy, as a consequence of supportive therapy with cytokines. It is well known that these bone marrow stimulants, such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor(filgastim, G-CSF), and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor(GM-CSF), and erythropoietin can cause diffusely increased FDG uptake in bone marrow (and in the spleen) on PET. Diffuse bone marrow uptake of FDG also has been reportd in patients with leukemia.
Splenic involvement with leukemia is more common with chronic forms of the disease and denotes a poorer prognosis.
Reference:
Takalkar A, Yu JQ, Kumar R, et al. Diffuse bone marrow accumulation of FDG in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia mimics hematopoietic cytokine-mediated FDG uptake on positron emission tomography.Clin Nucl Med. 2004 Oct; 29:637-9.
Endo T, Sato N, Koizumi K, et al. Localized relapse in bone marrow of extremities after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2004 Jul; 76(3): 279-82
Followup:
Left iliac crest bone marrow biopsy showed chronic myelocytic leukemia.
Major teaching point(s):
A detailed history is crucial for proper differential diagnosis of PET findings patients with known or suspected cancer.
Differential Diagnosis List
1.Anemia with marrow hyperplasia
2.Administration of bone marrow stimulants(G-CSF,GM-CSF and erythropoietin)
3.Diffuse osseous metastatic disease
4.Leukemia
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt138
Copyright by Wash U MO

