Case Author(s): Zhiyun Yang, M.D. and Barry A. Siegel, M.D. , 04/16/05 . Rating: #D3, #Q3
Diagnosis: Recurrent Breast Cancer
Brief history:
28-year-old woman with right breast cancer, now with local recurrence and undergoing restaging.
Images:
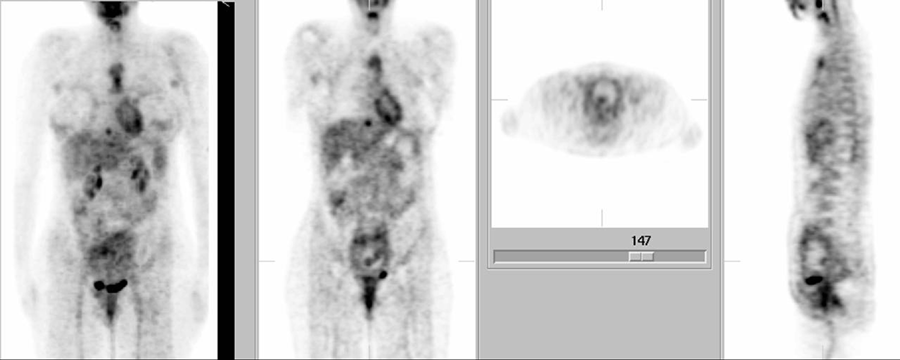
FDG-PET
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Coronal PET images
View third image(pt).
Sagittal PET images
View fourth image(pt).
Axial PET images
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Recurrent Breast Cancer
Full history:
28-year-old woman with right breast cancer diagnosed in 2002 and treated by lumpectomy in August, 2002. The patient had a recurrent tumor in the right breast and underwent bilateral mastectomy in September, 2003, followed by placement of breast implants. Multiple skin lesions were found in the right breast region about two weeks ago and biopsy of the skin lesions showed carcinoma. This PET study is for restaging prior to further treatment. Of note, the patient is pregnant (second trimester)
Radiopharmaceutical:
9.46 mCi F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose i.v.
Findings:
There is focally increased FDG uptake noted in the skin of the upper outer quadrant of the right breast and focally increased FDG uptake in the skin of the lower outer quadrant of the right breast; these findings are consistent with the patient's skin lesions demonstrated clinically. Increased FDG uptake is also noted in the manubrium and upper portion of the body of the sternum. Posterior to the manubrium on the left side, there is focal activity that likely represents metastatic lymphadenopathy in either a high internal mammary lymph node or a prevascular mediastinal lymph node. Focally increased FDG uptake is noted in both axillae, consistent with metastatic adenopathy. There is a focus of increased FDG uptake noted just above the diaphragm anteriorly and to the right side of the midline, likely representing metastasis in a pericardiac or epiphrenic node.
An enlarged uterus is noted with diffusely increased activity in its wall. Somewhat more intense uptake is seen along the posterior wall of the uterus, which likely represents the placenta. The dumbbell-shaped region of focally greater FDG uptake seen within the uterine cavity on the coronal image is likely in the fetal brain and myocardium/liver (the fetal head is down).
Discussion:
Because the patient was pregnant, a reduced dose of FDG (9.5 mCi) instead of the usual 15-mCi adult dose was used for the study (and imaging time was increased to compensate). Conventional PET rather than PET/CT was performed. Additionally, before administration of FDG, intravenous access was established to allow for vigorous intravenous patient hydration. Further, a Foley catheter was inserted into the urinary bladder. All of these steps were taken to minimize the fetal radiation dose (most of which is attributable to activity in the maternal bladder). Although diuretic administration also increases the rate of excretion of FDG, furosemide was not administered because its safety during pregnancy has been questioned. (It is labeled as "PREGNANCY CATEGORY C".)
The estimated fetal radiation dose from FDG recently has been updated to include the contribution from FDG that crosses the placenta and accumulates in fetal tissues. These dose estimates are shown below.
Early pregnancy 67 mrem/mCi
3 mo gestation 67 mrem/mCi
6 mos gestation 59 mrem/mCi
Term 57 mrem/mCi
These dose calculations assume a 2-hour post-injection voiding time. Thus, the additional steps taken to minimize urinary tract FDG activity in this patient likely substantially reduced the dose further.
Reference:
Stabin MG. Proposed addendum to previously published fetal dose estimate tables for 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med 2004; 45:634-5.
Followup:
Skin, right breast, punch biopsy.
- carcinoma consistent with breast primary, intermediate grade with lymphatic space invasion.
Major teaching point(s):
FDG-PET can be performed safely in a pregnant patient, if the risks are carefully considered and judged to be outweighed by the expected benefits of the study, and with attention to technical modifications designed to minimize the fetal radiation exposure.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Breast, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt135
Copyright by Wash U MO

