Case Author(s): Zhiyun (Jane) Yang, MD. and Keith Fischer, MD. , 04/04/05 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Hepatoblastoma
Brief history:
9-year-old girl with a new lesion.
Images:
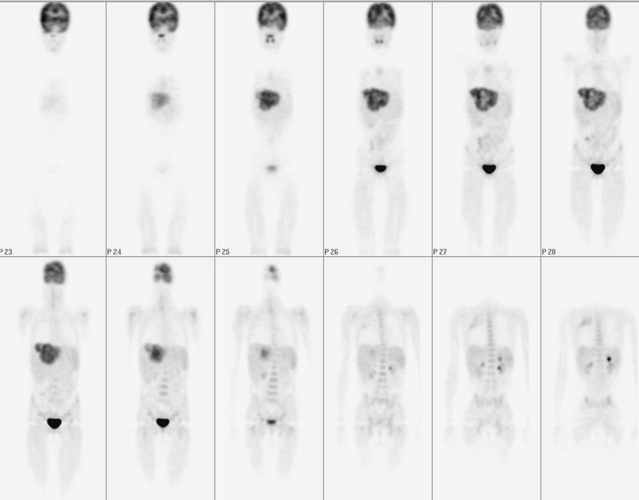
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) imaging of the body
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Axial PET image of the chest and upper abdomen.
View third image(ct).
Selected axial CT of the liver
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Hepatoblastoma
Full history:
9-year-old girl with newly diagnosed hepatoblastoma. She has not received any treatment. This study is for initial staging.
Radiopharmaceutical:
5.0 mCi F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose i.v.
Findings:
PET showed a large mass with markedly increased FDG uptake involving both lobes of the liver, consistent with the patient's known hepatoblastoma. There is a linear region of increased FDG uptake in the upper portion of the right chest posteriorly without a corresponding abnormal finding on the CT study or bone scintigraphy.
CT demonstrated that a large heterogeneous enhancing mass within both lobes of the liver consistent with the patient's known diagnosis of hepatoblastoma.
Discussion:
Hepatoblastoma is the most common liver cancer in children (79% of all liver tumors and almost two thirds of primary malignant liver tumors in children), although it is relatively uncommon compared to other solid tumors in children.
Complete surgical resection of the tumor at diagnosis, followed by adjuvant chemotherapy, is associated with 100% survival rates, but the outlook remains poor in children with residual disease after initial resection, even if they receive aggressive adjuvant therapy.
Pathophysiology: Hepatoblastomas originate from immature liver precursor cells and present morphologic features that mimic normal liver development. Hepatoblastoma is usually unifocal and affects the right lobe of the liver more often than the left lobe.
Metastases affect the lungs and the porta hepatis; bone metastases occur very rarely. CNS involvement has been reported at diagnosis and during relapse.
Followup:
LIVER, NEEDLE BIOPSY: small blue cell tumor with extensive coagulative necrosis, consistent with hepatoblastoma.
Differential Diagnosis List
Hepatoblastoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, malignant mesenchymal hepatic tumor (undifferentiated sarcoma, angiosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, rhabdoid tumor)
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Gasterointestinal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt133
Copyright by Wash U MO

