Case Author(s): Feiyu Xue, M.D., Ph.D. and Jerold Wallis, M.D. , 6/29/04 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Adrenal cortical carcinoma
Brief history:
65 year old woman was found to have a large retroperitoneal mass.
Images:
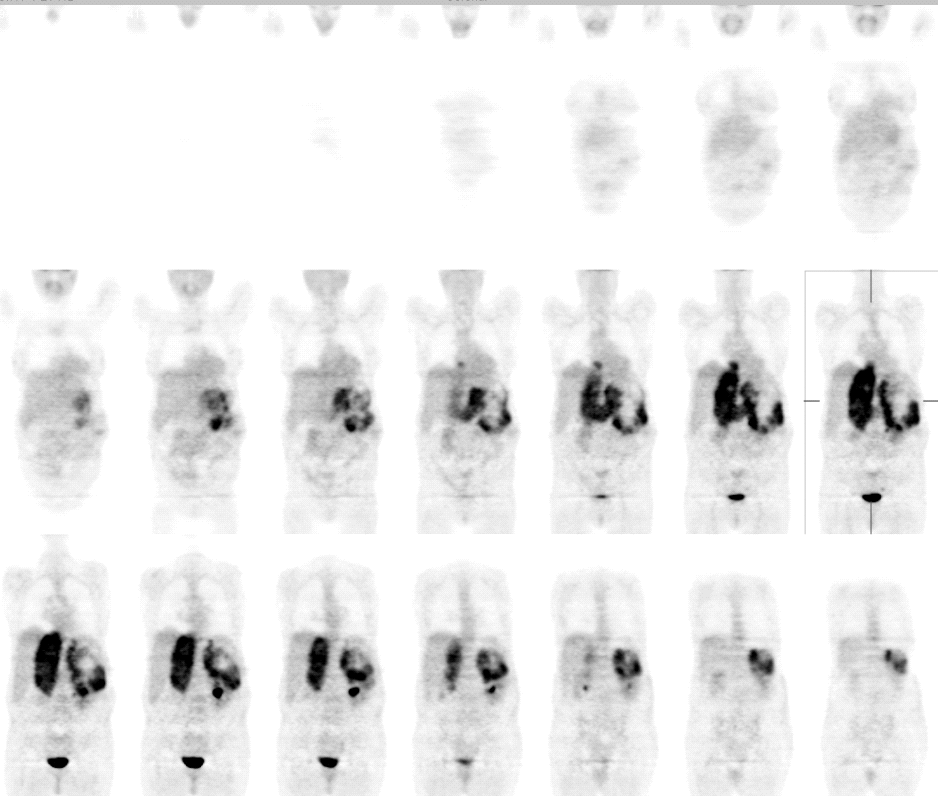
Coronal image of FDG-PET
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Axial image of FDG-PET
View third image(pt).
Fusion image of PET/CT
View fourth image(pt).
Fusion image of PET/CT
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Adrenal cortical carcinoma
Full history:
65 year old woman was found to have a large retroperitoneal mass on the left, either arising from the left adrenal or kidney. PET was requested for further evaluation.
Radiopharmaceutical:
15 mCi F-18 FDG
Findings:
There is a left upper quadrant soft tissue mass in the retroperitoneal space. It is displacing the kidney inferiorly, and the stomach and pancreas superiorly. On PET, there is intense uptake along the periphery of the mass, with decreased uptake centrally consistent with tumor necrosis. The inferior vena cava is markedly expanded and there is intensely increased FDG uptake within the inferior vena cava, consistent with tumor invasion of IVC. The tumor is seen extending into the right atrium.
Discussion:
Adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC) is a rare malignant neoplasm with a poor prognosis. The sensitivity/specificity of PET in detection and staging of ACC has not been well studied. However, one study of small sample of patients has found sensitivity and specificity of PET in ACC was 100% and 97%, respectively. PET altered or influenced the tumor stage in 3/10 patients, modifying the subsequent therapeutic management in 2/10 patients. These authors conclude that FDG-PET is highly useful in ACC and should be included in the work-up for initial staging as well as for follow-up.
Reference:
Becherer A, Vierhapper H, Potzi C, Karanikas G, Kurtaran A, Schmaljohann J, Staudenherz A, Dudczak R, Kletter K. FDG-PET in adrenocortical carcinoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2001 Aug;16(4):289-95.
Followup:
MIR of abdomen and pelvis confirm origin of tumor from the left adrenal rather than the left kidney.
View followup image(mr).
MIR of abdomen and pelvis. Upper 6 images are adrenal HASTE sequence, and lower 6 images are renal VIBE sequence.
Major teaching point(s):
Adrenal cortical carcinoma demonstrates increased FDG uptake. FDG PET is useful in ACC diagnosis and staging.
Differential Diagnosis List
Adrenal cortical carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma
Retroperitoneal sarcoma
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Genitourinary System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt106
Copyright by Wash U MO

