Case Author(s): Feiyu Xue, M.D., Ph.D., Tom R. Miller, M.D., Ph.D. , 4/7/2004 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Artifact from biliary stent
Brief history:
57-year-old woman with a history of metastatic breast cancer.
Images:
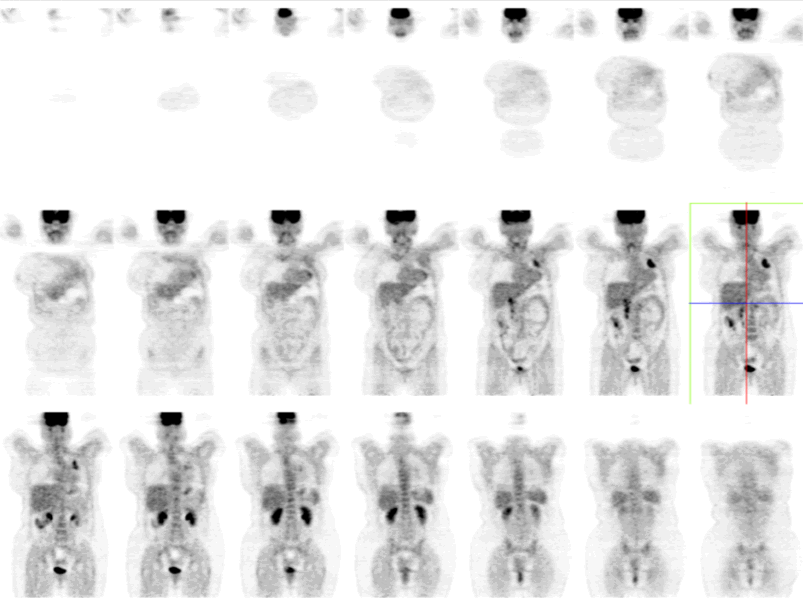
Coronal images of FDG-PET.
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Fusion images of PET/CT.
View third image(xr).
Frontal radiograph of the lumbar spine.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Artifact from biliary stent
Full history:
57 year old woman with history of metastatic breast cancer presents for restaging after chemotheraphy. She has a known left upper lobe mass in the lung from metastasis. In addition, she has a history of biliary obstruction from nodal metastasis to the porta hepatis with biliary stent placement.
Radiopharmaceutical:
F-18 FDG i.v.
Findings:
The main image (coronal image of FDG-PET) and fusion images demonstrate an intense focus of FDG uptake in the left upper lobe of the lung, consistent with known metastasis. In addition, there is linear FDG activity in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen at the site of the common bile duct. Both the CT and radiograph of the lumbar spine demonstrate a biliary stent within the common bile duct. Non-attenuation corrected images (not shown here) show less intense activity in the same area, indicating the activity on attenuation corrected images is primarily due to attenuation correction artifact, and to a lesser degree due to inflammation.
False positive activity can be seen on PET/CT arround metallic objects such as a pacemaker or orthopedic prosthesis on attenuation corrected images. This attenuation correction artfact can be confirmed by comparing the attenuation corrected images with the non-attenuation corrected images. In this case, mild activity arround the biliary stent on non-attenuation corrected images is likely due to inflammatory response to metallic stent in the common bile duct.
Reference:
Bujenovic S, Mannting F, Chakrabarti R, Ladnier D. Artifactual 2-deoxy-2
Major teaching point(s):
Attenuation correction can produce false-positive activity on PET/CT arround metallic objects such as a pacemaker or orthopedic prosthesis. Interpretators of PET/CT need to be aware of this artifact. The artifact can be confirmed by comparing the attenuation corrected images with the non-attenuation corrected images.
Differential Diagnosis List
The differential diagnoses includes inflammation around the biliary stent. Neoplasm is unlikely as the activity is linear and conforms to the shape of the stent.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Gasterointestinal System, Category:Other(Artifact))
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt104
Copyright by Wash U MO

