Case Author(s): Yonglin Pu, MD,Ph.D, Farrokh Dehdashti,MD. , 03/22/03 . Rating: #D3, #Q4
Diagnosis: B-Cell Lymphoma in the Central Nervous System
Brief history:
70 year old with a three month history of mental status change, dementia, tremor, gait instability and falling.
Images:
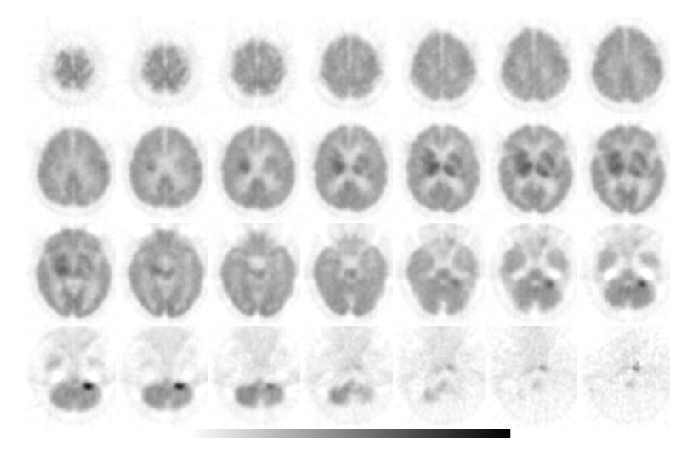
Tumor PET Imaging (metabolism), axial slices
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
Tumor PET Imaging (metabolism), coronal slices
View third image(mr).
MRI of the Brain, T1WI with Gadolinium
View fourth image(mr).
MRI of the Brain,T2WI
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: B-Cell Lymphoma in the Central Nervous System
Full history:
70 year old with a three month history of mental status change, dementia, and falling. He also presents with tremor and gait instability. This study is performed for further diagnosis.
Radiopharmaceutical:
15.0 mCi F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose i.v.
Findings:
There is an area of intense FDG uptake in the right basal ganglia (and possibly left basal ganglia), right internal capsule extending to the right thalamus and left thalamus. These findings correlate with the contrast-enhanced lesion demonstrated on the MR images performed 3 days ago. In addition, there is intense FDG uptake in the left cerebellar hemisphere, which correlates with the contrast enhanced lesion demonstrated on the MR images.
Discussion:
Primary CNS lymphoma, a very rare brain neoplasm in the past, is now one of the most common tumors of the central nervous system (CNS), representing 6.6%-15.4% of all primary brain tumors. The prevalence of primary CNS lymphoma is similar to that of meningioma and low-grade astrocytoma. It can occur in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent people. Supra-tentorial CNS lymphomas occur more often than those in the posterior fossa. It can also involve leptomeninges. Dural involvement by primary CNS lymphoma is rare . Spinal cord invlovements constitute about 1% of primary CNS lymphomas. The characteristic appearance of CNS lymphoma on FDG-PET images is that of a white matter lesion near the ventricles with intense FDG uptake ( equal or greater than that of normal gray matter). Basal ganglia lesions are also common. The inflammatory condition, such Toxoplasmosis normally has less uptakes. FDG-PET has been shown to be extremely useful in differentiating toxoplasmisis from lymphoma in patients with AIDS. Please refer to other cases of CNS lymphoma in our digital teaching file.
Reference
Koeller KK. Smirniotopoulos JG. Jones RV. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation.Raduographics 1997;17(6):1473-526
Pierce et al., Ann Intern Med 1995; 123:594-8.
Followup:
Craniotomy biopsy showed malignant lymphoma, large B-cell type.
Major teaching point(s):
FDG-PET is useful in the identifying CNS lymphoma
Differential Diagnosis List
Glioblastoma multiforme, metastasis, radiation necrosis, infectious diseases
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Skull and Contents, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt089
Copyright by Wash U MO

