Case Author(s): Lisa M. Oakley, M.D. and Barry A. Siegel, M.D. , 12/31/97 . Rating: #D3, #Q3
Diagnosis: Effect of Hyperinsulinemia on FDG Distribution
Brief history:
Elderly man with a remote history of colon cancer.
Images:
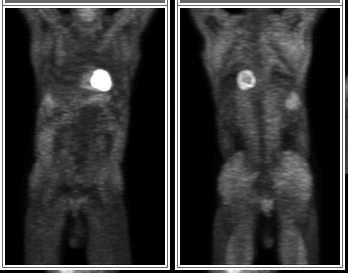
ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR FDG-PET REPROJECTION IMAGES OF THE BODY (FIRST STUDY)
View main image(pt) in a separate image viewer
View second image(pt).
ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR FDG-PET REPROJECTION IMAGES OF THE BODY (2ND STUDY)
View third image(ct).
AXIAL CT IMAGE THRU LIVER
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Effect of Hyperinsulinemia on FDG Distribution
Full history:
75-year-old man with a history of colon cancer resected seven years
ago. CT of the abdomen performed to evaluate newly diagnosed
prostate cancer revealed a new hepatic lesion and FDG-PET was requested
to evaluate the mass and extent of disease.
Radiopharmaceutical:
F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
Findings:
Initial attenuation-corrected PET reprojection images show significant diffuse skeletal muscle and
myocardial uptake. The internal organs are difficult to evaluate because of
the significant soft tissue uptake and poor visceral organ uptake of FDG.
However, an ill-defined focus of increased uptake is seen in the right lobe of the
liver. The patient's serum glucose level was within the normal range (80 mg/dL),
but on further questioning, the patient revealed that he had eaten
breakfast only 2 hours before this study.
A repeat PET study was performed two days later with the patient in a
fasting state. The usual distribution of activity is now seen, with
improved resolution of the internal organs, decreased skeltal muscle
uptake and decreased myocardial uptake. The lesion within the liver
is more easily seen and more well defined. No additional abnormal
foci of increased uptake are seen.
CT scan through the upper abdomen reveals a 4 x 5 cm. heterogeneous low-density
mass within the right lobe of the liver. This mass correlates
with the focus of intensely increased FDG uptake seen on PET and is consistent
with metastatic disease.
Discussion:
Careful attention to patient preparation is critical for PET imaging. FDG is a glucose analogue that is
taken up by glucose membrane transporters on the cell surface of both
normal and tumor cells. Uptake of FDG and glucose into malignant cells is
facilitated by increased expression of these glucose transporters on the
cell surface. If one understands the physiologic basis for
FDG distribution in the body, it becomes clear that the patient must be fasting
for at least 4-6 hours before injection to assure that serum glucose and
insulin levels are at physiologic minimums. Before proceeding with
the study, the patient's serum glucose should be checked and one should
confirm that the patient has been fasting. The effect of hyperglycemia
on FDG uptake is two-fold. First, increased circulating glucose acts as a competitive inhibitor of
FDG uptake by direct competition for glucose transporters on the cell
surface. This results in a lower cellular concentration of FDG
to be imaged by PET and poorer imaging statistics in the organs and
tissues of interest (including malignant tumors). Secondly, hyperglycemia
stimulates insulin release and circulating insulin preferentially drives glucose and
FDG into skeletal muscle. Additionally, myocardial uptake of FDG is
greater when blood glucose levels are increased and when hyperinsulinemia
secondarily reduces blood free fatty acid concentrations. Less FDG is
then available to accumulate in tumor cells.
Thus, despite a normal serum glucose level in this patient prior to
FDG injection, significant skeletal muscle and myocardial uptake occured
in the first study, presumably as a result of hyperinsulinemia.
REFERENCES :
Rigo P, Paulus P, Kaschten BJ et al. Oncological applications of positron
emission tomography with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose. Eur J Nucl Med
1996; 23:1641-1674.
Torizuka T, Fisher SJ, and Wahl RL. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia
decreases uptake of 2-(F-18)-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose into experimental
mammary carcinoma. Radiology 1997; 203:169-172.
Torizuka T. Clavo AC. Wahl RL. Effect of hyperglycemia on in vitro
tumor uptake of tritiated FDG, thymidine,L-methionine and L-leucine.
J Nucl Med 1997; 38:382-386.
Followup:
The patient underwent a right hepatectomy, which revealed a
moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma consistent with metastasis
from the patient's known colon cancer primary.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Tumor Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Gasterointestinal System, Category:Other(Artifact))
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pt018
Copyright by Wash U MO

