Case Author(s): Daniel E. Appelbaum, MD and Farrokh Dehdashti, MD , 6/13/00 . Rating: #D3, #Q4
Diagnosis: Meningeal carcinomatosis
Brief history:
56 year-old female with history of metastatic breast cancer who presented with mental status changes.
Images:
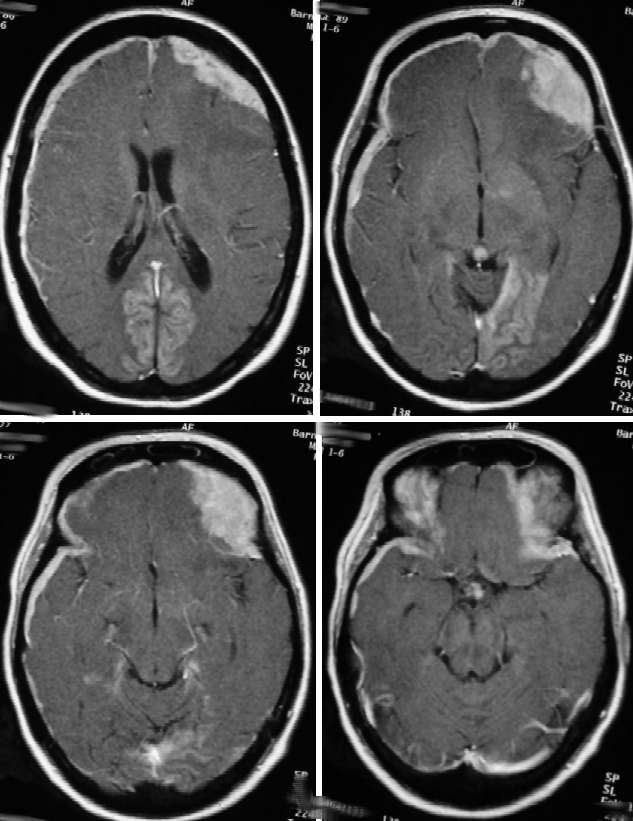
Selected axial T1-weighted post-contrast images are shown.
View main image(mr) in a separate image viewer
View second image(mr).
Selected axial T2-weighted images.
View third image(pb).
Axial images from FDG brain PET.
View fourth image(pb).
Selected axial image from brain PET (inverted greyscale).
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Meningeal carcinomatosis
Full history:
This is a 56 year-old female with known metastatic breast carcinoma and mental status changes. Brain MR and PET were obtained for further evaluation.
Radiopharmaceutical:
10.0 mCi F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) i.v.
Findings:
The MRI demonstrates extensive abnormal dural enhancement with more focal meningeal thickening in the left frontal region. These findings were compatible with diffuse carcinomatosis. Vasogenic edema of the left frontal lobe is also present suggesting intra-axial invasion.
Before radiation therapy of the brain was performed, confirmatory evidence of carcinomatosis was desired. The patient was significantly thrombocytopenic, making lumbar puncture or brain biopsy risky. A brain PET was requested.
The PET examination demonstrates increased FDG activity corresponding to the generalized meningeal enhancement as well as to the focal thickening. These findings are also compatible with carcinomatosis. Note also the decreased metabolic activity in the left frontal lobe from the vasogenic edema.
Discussion:
This is an unusual indication for brain PET but provides a good example of this entity. One caveat deserves mention: FDG-PET can be nonspecific as any active inflammatory or infectious process can be FDG-avid. By these images alone, infectious menigitis with a more focal subdural abscess would be a possibility, but the history supports the diagnosis of carcinomatosis.
Followup:
The patient was subsequently treated with radiation therapy.
Major teaching point(s):
FDG-PET is a useful test to confirm meningeal carcinomatosis when biopsy is not possible.
Differential Diagnosis List
Meningeal infectious or inflammatory disease.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of PET Brain (Nontumor) Imaging Studies (Anatomic field:Skull and Contents, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: pb008
Copyright by Wash U MO

