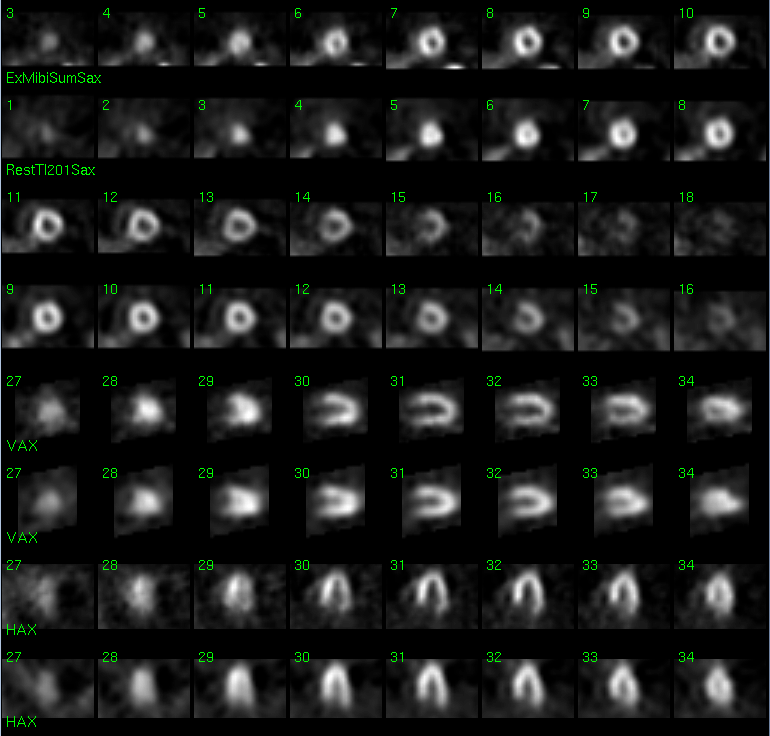

Tomographic images from Myocardial SPECT during pharmacologic stress with adenosine and Tc99m-Sestamibi (TOP) and Rest with 201-Thallium Chloride (BOTTOM)
View main image(mi) in a separate image viewer
View second image(mi). Quantitative Perfusion Data
View third image(mi). Gated Myocardial Perfusion Report
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
She specifically denies any chest discomfort at any time, and she denies any shortness of breath, though her exercise tolerance is limited by her hip pain. She denies palpitations, light-headedness, presyncope, or syncope, as well as orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, or any other cardiovascular complaints. She does have some mild lower extremity edema occasionally.
The electrocardiogram during infusion of adenosine was positive for ischemia, with 1-2 mm ST depression in lead II, III, AVF, V3, V4, and V5 which persisted for approximately 9 minutes after infusion of the agent.
Transient Ischemic Dilitation is present when the cardiac chamber size enlarges or becomes dilated during stress. The pathophysiology behind this is complex, but involves decompensation of the myocardium during maximal stress due to underlying ischemia that results in chamber dilitation that can then be detected. The actual ischemic changes, typical reversible perfusion defects, are not necessarily detectable when the ischemia is "balanced", involving the entie myocardium, since there are no areas of relative decreased perfusion when ischemia is diffuse and balanced. In this setting, the presence of transient ischemic dilitation (TID) may be the only indicator of extensive coronary artery disease with ischemic myocardium.
Angiographic findings are detailed below:
Right Coronary System: The right coronary artery is dominant. It has an ostial 65-70% lesion and is calcified such that when it is intubated with a 4F 1.3 mm diameter right Judkins catheter the pressure drops from 160 mmHg to 80 mmHg during injection and so there is an 80 mm gradient across the right coronary ostium which is at least 80% narrowed. Just beyond the bifurcation the right coronary artery has high grade 85% stenosis. The distal lumen is suitable for bypass grafting.
Left Coronary System: 1. The left coronary system consists of the calcified left main coronary artery bifurcating into the left anterior descending and circumflex coronaries. An intermediate branch and a diagonal are also seen. 2. The ostium of the circumflex coronary artery is high grade at least 85-90%. The left anterior descending/diagonal bifurcation is also high grade at least 85% and the proximal diagonal best seen in the AP caudal view is also high grade at least 85%. The distal calibers of the left anterior descending, the diagonal, the distal diagonal, the proximal diagonal, and the circumflex marginal system as well as the right coronary artery are suitable for bypass grafting.
DIAGNOSTIC IMPRESSION: Severe triple vessel disease involving high grade proximal lesions
References and General Discussion of Myocardial Imaging (Anatomic field:Heart and Great Vessels, Category:Organ specific)
Return to the Teaching File home page.