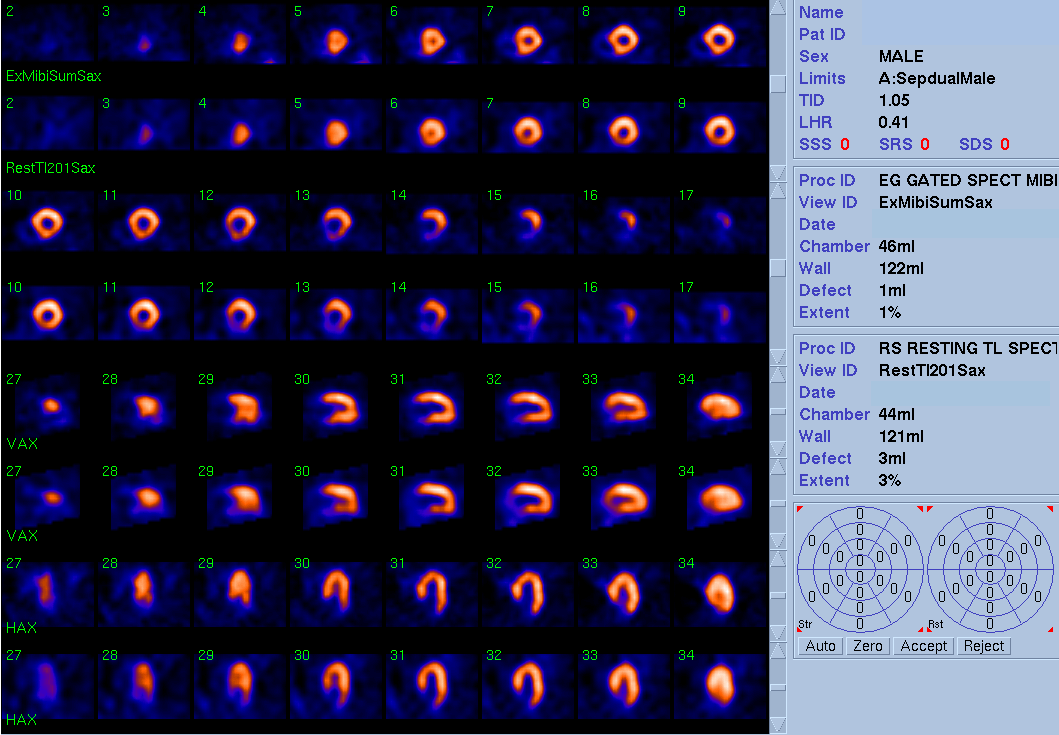

Splash images of myocardial perfusion study.
View main image(mi) in a separate image viewer
View second image(mc). Baseline ECG
View third image(mc). ECG at 00:57 minutes after start of adenosine infusion
View fourth image(mc). ECG at 1:07 minutes after start of adenosine infusion
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
The patient was originally scheduled as an adenosine stress test with myocardial perfusion imaging. The adenosine test was aborted due to the development of complete heart block (see 3rd ECG above), at which time the infusion was stopped. A dobutamine stress test was subsequently performed, during which the patient achieved 91% of predicted maximum heart rate without symptoms and no evidence of ischemia on the dobutamine stress ECG.
During the adenosine stress test, the patient developed complete heart block and became unresponsive. The adenosine infusion was immediately discontinued with full recovery of the patient within minutes. No further interventions required. The patient then underwent a dobutamine stress test without further incident.
This study illustrates the importance of monitoring patients during cardiac stress testing. Adenosine causes slowing of conduction across the atrioventricular node; therefore, patients with first-degree AV block must be closely monitored for the development of complete heart block. This complication is easily reversed by immediately stopping the adenosine infusion. If the heart block persists, aminophylline or atropine can be administered to reverse the effects of the adenosine.
In choosing which type of pharmacologic stress test to order, it is important to consider the patient's clinical status. The presence of a 1st degree heart block is not an absolute contraindication to adenosine stress test; however, since adenosine slows conduction at the AV node and hence is the only agent that can induce heart block, these patients require especially close monitoring during an adenosine stress test. Dipyridamole, which blocks re-uptake of adenosine that leads to elevated adenosine levels, rarely causes heart block because the adenosine levels achieved are not as high as that seen with infusion of adenosine. Dobutamine is a synthetic catecholamine with inotropic and chronotropic effects, leading to increased sinoatrial and atrioventricular node conduction and ectopy; the risk of developing arrhythmias is higher with dobutamine than with the vasodilating agents.1
1. Leppo JA. Comparison of pharmacologic stress agents. J Nucl Cardiol 1996;3:S22-26.
References and General Discussion of Myocardial Imaging (Anatomic field:Heart and Great Vessels, Category:Other generalized systemic disorder)
Return to the Teaching File home page.