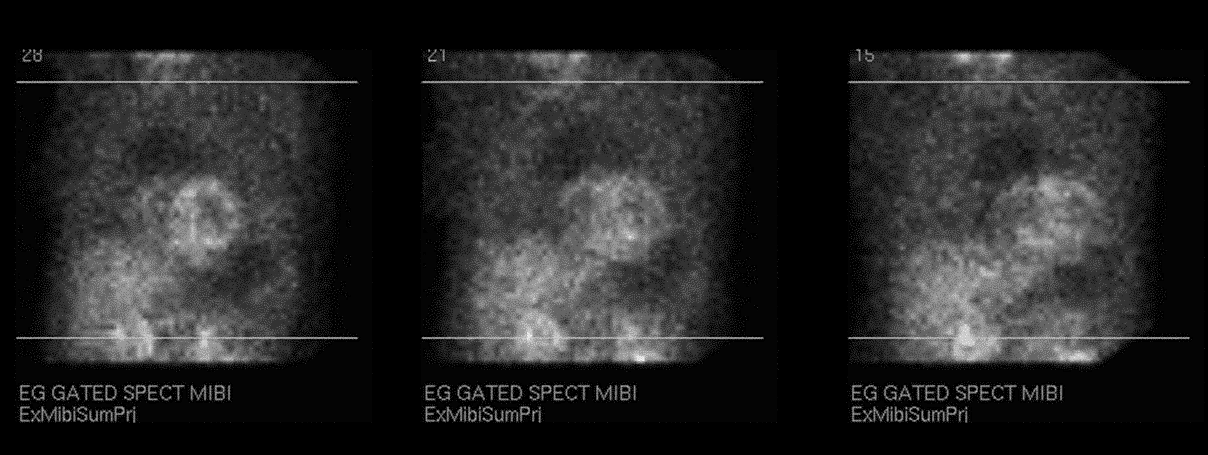

Raw projection data from a myocardial perfusion scintigraphy performed with Tc-99m sestamibi (L LAT-LAO-RAO)
View main image(mi) in a separate image viewer
View second image(mi). Slice display from SPECT myocardial perfusion scintigraphy
View third image(mi). ECG-gated display from SPECT myocardial perfusion scintigraphy
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
The slice display shows a large, moderately reversible perfusion defect of mild severity in the lateral wall indicating a mixed lesion of infarction and ischemia. There is also a moderate-sized, nonreversible perfusion defect of moderate severity in the anteroapical wall due to infarction.
The ECG-gated images demonstrates moderate to marked left ventricular enlargement and a left ventricular ejection fraction of 33%.
This is an obvious abnormality only if you look at the projection images. It is preferable to begin evaluation of myocardial perfusion images with the cine display of these images, typically to assess for motion or prominent liver or bowel uptake, although as in this case other important abnormalities may only be seen in this format.
At subsequent cardiac catheterization, the pseudoaneurysm was found to be superior to and not involving the coronary arteries or the bypass grafts. Also, the left anterior descending artery was occluded after small septal and diagonal branches. The left internal mammary artery to LAD graft was patent but the distal LAD was thread-like and small with marked diffuse plaque. The circumflex coronary artery was small and diffusely diseased. The radial artery graft to several distal circumflex vessels was without significant lesion.
Surgical repair confirmed there was no involvement of the coronary arteries or bypass grafts by the pseudoaneurysm.
View followup image(ct). CT images of the thorax
References and General Discussion of Myocardial Imaging (Anatomic field:Heart and Great Vessels, Category:Effect of Trauma)
Return to the Teaching File home page.