Case Author(s): Stephanie P.F. Yen, M.D. and Henry D. Royal, M.D. , 11/14/97 . Rating: #D2, #Q4
Diagnosis: Thymoma
Brief history:
62-year-old male with a history of coronary artery disease who
presents with dyspnea on exertion and EKG changes.
Images:
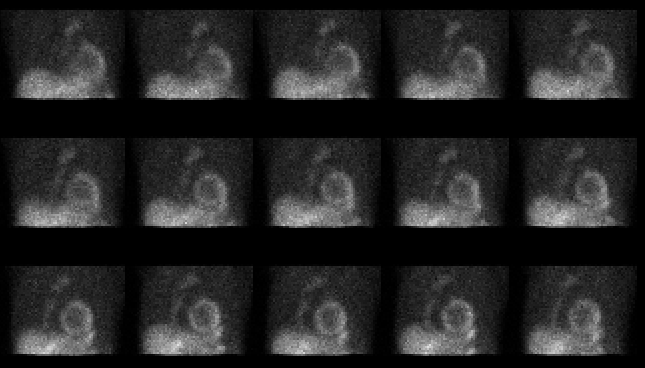
Selected images from the raw projection data acquired during the exercise
portion of the myocardial perfusion study.
View main image(mi) in a separate image viewer
View second image(ct).
Axial image of chest from contrast-enhanced computed tomography
View third image(xr).
Posteroanterior chest
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Thymoma
Full history:
62-year-old male with history of prior myocardial infarction who
presents with dyspnea on exertion and EKG changes.
Myocardial perfusion imaging was requested to evaluate for myocardial
viability.
Radiopharmaceutical:
3.3 mCi Tl-201 chloride, i.v.; and 20.6 mCi Tc-99m sestamibi, i.v.
Findings:
Selected images from the raw projection data acquired during the
exercise portion of the myocardial perfusion imaging examination
demonstrate a focus of increased activity in the retrosternal region.
On the resting thallium projection data (not shown), a similar focus of
increased activity is identified in the retrosternal region.
The patient subsequently underwent a computed tomography study of the
chest on 12-01-97, which revealed a 2.8 X 4.2 X 4.0 cm homogeneously
enhancing anterior mediastinal mass at the level of the carina as well as a
small right pleural effusion. The mass was not contiguous with the
thyroid. No significant mediastinal lymphadenopathy
was seen. The computed tomographic appearance of this mass suggests
the primary differential considerations of lymphoma and thymoma.
Posteroanterior chest radiograph performed on 1/12/98 shows a subtle
contour abnormality in the region of the aortopulmonary window,
corresponding to the patient's known anterior mediastinal mass. The mass
is not well visualized on the lateral view (not shown).
Discussion:
The projection images from a myocardial perfusion imaging study are
used to assess the technical quality of the
examination, providing information on patient motion, as well as to
confirm the presence of attenuation of myocardial activity by breast
tissue or diaphragm
suspected on the standard tomographic images. In addition, as this case
illustrates, the projection data also allow for a survey of the entire
thorax and axillae for abnormal extracardiac radiopharmaceutical
accumulation. Both thallium-201 and Tc-99m methoxyisobutyl isonitrile
(MIBI) have been shown to accumulate in pulmonary malignancies, breast
tumors, lymphomas, and bone and soft tissue sarcomas. Abnormal axillary
accumulation of Tc-99m sestamibi may reflect the presence
of nodal metastases or the presence of significant extravasation of
radiopharmaceutical at the time of injection.
The diagnosis of such clinically significant findings may be missed if
only standard tomographic images are reviewed.
Cases have been reported in the literature demonstrating the accumulation
of Tc-99m sestamibi and thallium-201 in thymomas. Thymomas originate
from the thymic epithelium and are most common in the anterior
mediastinum. Thymomas may be encapsulated and noninvasive, or they may
demonstrate invasion into the surrounding tissues or metastasize locally,
with the pleura and pericardium being the most frequent sites. No
histological difference has been demonstrated between those tumors
that are noninvasive, invasive, or metastatic. The distinction between
a "benign" or "malignant" thymoma is based on the absence or presence of
invasiveness, respectively.
Patients with thymomas are usually 40 to 60 years of age and may present
with nonspecific symptoms related to
the presence of an anterior mediastinal mass, such as cough, dyspnea,
chest discomfort, and dysphagia. Many syndromes and diseases have been
shown to have an association with thymomas. Of these, myasthenia gravis,
red cell aplasia, and hypogammaglobinemia are the most common. It is
reported that surgical resection is the most effective treatment.
References: 1. Rosenberg JC. Neoplasms of the Mediastinum. In:
Devita VT, Hellman S, and Rosenberg SA. Cancer Principles & Practice
of Oncology, 4th ed. J.B. Lippincott Co., Philadelphia, PA, 1992:
764-769. 2. Adalet I, Kocak M, Ece T et al. Tc-99m MIBI and Tl-201
uptake in a benign thymoma. Clinical Nuclear Medicine. 20:733-734, 1995.
3. Campeau RJ, Ey EH, and Varma DGK. Thallium-201 uptake in a benign
thymoma. Clinical Nuclear Medicine. 11:524, 1986.
Followup:
A fine needle aspirate biopsy of the anterior mediastinal mass was
performed under computed tomography guidance on 12/18/97. Pathology
revealed features consistent with thymoma. Pathology remarked that FNA
cytology cannot determine if the thymoma is invasive or malignant, nor
can it determine the future behavior of the lesion. The patient
subsequently underwent a thymectomy on 1/13/98. Pathology demonstrated
thymoma, predominantly epithelial spinde cell type, with evidence of
microinvasion of the capsule. None of the three regional lymph nodes sampled
showed evidence of tumor (stage T2N0M0).
Major teaching point(s):
This case emphasizes the importance of viewing the projection images
of myocardial perfusion imaging studies. Not only do the projection
images provide information about patient motion during the exam and confirm
the presence of attenuation of myocardial activity by breast tissue or
diaphragm, but they also may reveal extracardiac abnormalities of the thorax which may be
missed on the standard SPECT myocardial perfusion images.
Differential Diagnosis List
The classic differential diagnosis of an anterior mediastinal mass includes
thymoma, lymphoma, germ cell tumors, and thyroid pathology.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Myocardial Imaging (Anatomic field:Lung, Mediastinum, and Pleura, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: mi012
Copyright by Wash U MO

