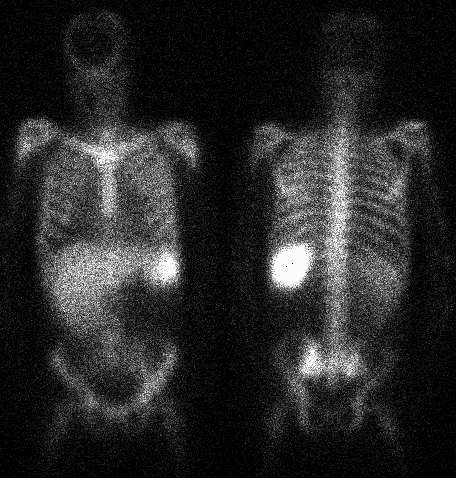

Anterior and posterior whole body images
View main image(iw) in a separate image viewer
View second image(iw). Coronal slices from the In-111 WBC SPECT of the pelvis (orientation: right-left)
View third image(ct). Bone windows from a CT of the pelvis
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Correlation was made with the patient's pelvis CT, which demonstrated findings of Paget's disease in the right iliac bone. The patient also had a chest xray (not shown), which demonstrated a moderate sized right pleural effusion. The left lung field was normal on the chest xray.
Indium WBC's normally distribute in the spleen more than the liver, in the lungs on the 4 hour image, and in the marrow. Other foci of accumulation are evidence of inflammation or infection. Paget's disease decreases the amount of bone marrow in the involved bone, so the abnormality is decreased WBC accumulation in the right iliac bone.
Similarly, there is apparently less activity in the right lung. Although this asymmetry could be due to slight inflammation in the left lung, followup chest radiographs failed to demonstrate any left lung abnormality. This asymmetry is most likely secondary to attenuation by the right pleural effusion (most evident on posterior images during supine imaging, due to layering of the effusion).
References and General Discussion of Indium -111 WBC Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Metabolic, endocrine, toxic)
Return to the Teaching File home page.