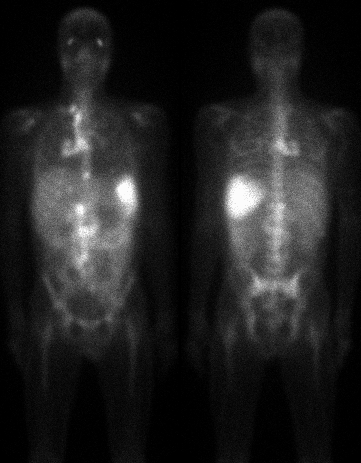
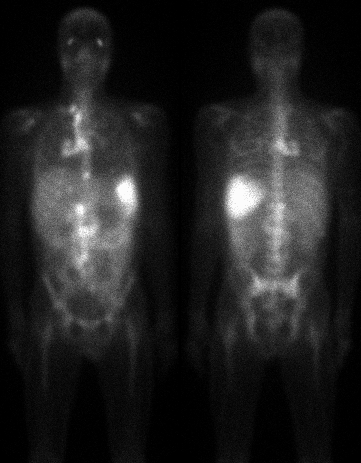
Anterior and posterior gallium images 72 hours after injection
View main image(ga) in a separate image viewer
View second image(ct). Axial CT image near level of SMA origin
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
15% to 25% of the administered dose is excreted by the kidneys during the first 24 hours. Renal activity on images obtained after 48 hours is abnormal. After 24 hours, the colon is the main route of gallium elimination. The colon, which is the critical organ, receives 0.6-0.9 rads/mCi.
Tumors with transferrin receptors on their surfaces will be gallium-avid. The gallium-transferrin complex is deposited intracellularly.
Gallium scintigraphy plays an important role in the clinical management of patients with AIDS who have fever or respiratory symptoms. This is particularly important in light of the high prevalence of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) in AIDS patients and the high sensitivity (90-96%) of gallium- 67 studies for PCP. While diffuse interstitial infiltrates on chest radiographs may be seen in early cases of PCP, mild prolonged symptoms and normal chest radiographs are common. Kramer, et al., found that 27 of 57 abnormal gallium lung scintigrams were associated with normal chest radiographs. Thus, chest radiographs have a relatively low sensitivity for detecting early lung disease in AIDS patients.
Negative gallium scintigraphy with a positive chest radiograph, however, is often associated with pulmonary Kaposišs sarcoma.
Gallium scintigraphic findings of PCP are diffuse pulmonary uptake distributed either heterogeneously or homogeneously. The sensitivity and specificity of gallium-67 scintigraphy for PCP are 90% and 75%, respectively. While the positive predictive value of abnormally increased pulmonary uptake is only about 60%, the negative predictive value for PCP in a patient with normal gallium scintigraphy is greater than 90%. Therefore, normal gallium scintigraphy makes the diagnosis of PCP very unlikely.
Gallium-67 citrate is also accumulated in other opportunistic infections in AIDS patients, including: disseminated mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (MAI), Candida esophagitis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), cryptococcus, and herpes simplex infections. Gallium-67 also accumulates in lymphoma and uncomplicated bacterial pneumonias, which are both very common in patients with AIDS.
References: 1) Sandler, et al. Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine, 1996. Williams and Wilkins 2) Datz, et al. Nuclear Medicine: a teaching file, 1992. Mosby Yearbook
References and General Discussion of Gallium Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Vascular and Lymphatic Systems, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Return to the Teaching File home page.