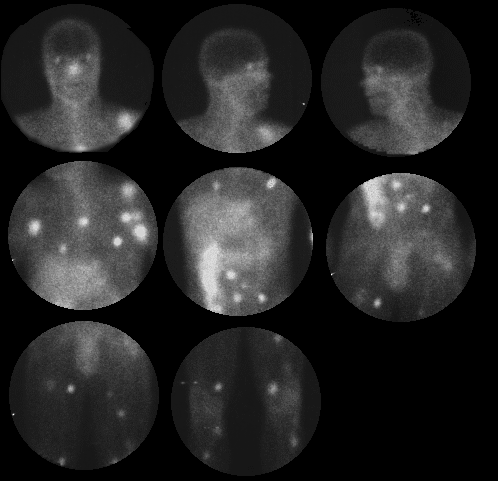
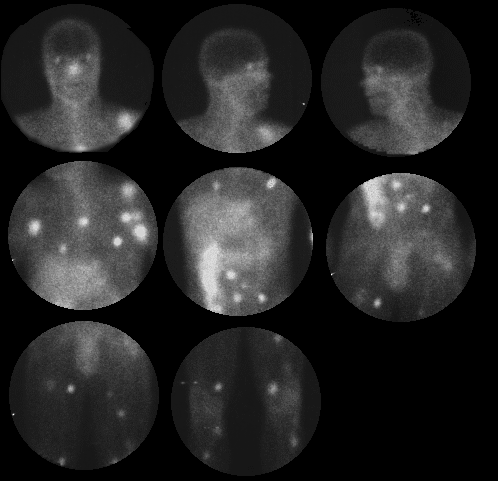
Anterior 72-hour delayed images.
View main image(ga) in a separate image viewer
View second image(ga). Posterior 72-hour delayed images.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
This examination reveals multiple foci of markedly increased activity throughout the upper extremities, axilla, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and lower extremities, bilaterally. Careful examination reveals the superficial nature of some of these lesions. In addition, abnormally increased activity is noted in the kidneys bilaterally.
2. The physical half-life is 78 hours and the biologic half-life is 2 - 3 weeks. Tumor doses are usually 8 - 10 mCi, and imaging is performed 48, 72, or possibly 96 hours after intravenous injection.
3. Gallium-avid tumors include Hodgkins lymphoma, non-Hodgkins lymphoma, hepatoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Burkitts lymphoma, testicular carcinoma, lung carcinoma and malignant melanoma.
4. Types of malignant melanoma include lentigo maligna, with low invasiveness and low metastatic potential. Superficial spreading melanoma carries an intermediate prognosis. Nodular melanoma is generally considered the most lethal. Malignant melanoma represents 1% of all cancers. These tumors arise from melanocytes derived from neural crest cells.
5. The Clarke grading system determining the 5 year survival with the depth of invasion is as follows:
Level I - In situ - 100%
Level II - Within papillary dermis - 100%
Level III - Extending to reticular dermis - 88%
Level IV - Invading reticular dermis - 66%
Level V - Subcutaneous infiltration - 15%
6. Breslow Staging:
Thin < 0.75 mm depth of invasion
Intermediate 0.76-3.99 mm depth of invasion
Thick > 4 mm depth of invasion
7 Metastatic Disease:
-May occur up to 20 years after inital diagnosis
-Bone involvement is often the initial manifestation of recurrence and has a poor prognosis.
-Lung involvement is seen in nearly 3 out of 4 cases at autopsy; is the most common site of relapse; and, leads to respiratory arrest (the most common cause of death).
-Liver lesions are common, especially at autopsy; and, may calcify.
8. Bilateral, diffusely-increased renal activity on gallium scintigraphy is considered abnormal after fourty-eight hours. This finding is nonspecific. Chemotherapy, acute tubular necrosis, acute renal failure, infections, infiltrative processes, vasculitis, metastatic involvement, and severe hepatocellular disease or saturated iron binding can be responsible for this type of finding.
2. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (less likely)
3. Multiple abscesses / decubiti (unusual)
4. Sarcoidosis, with cutaneous involvement (unusual)
5. Other gallium avid tumors with metastatic foci (unlikely)
References and General Discussion of Gallium Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Return to the Teaching File home page.