Case Author(s): Eric Hutchins, M.D. and Tom R. Miller, M.D., Ph.D. , 11/10/04 . Rating: #D., #Q.
Diagnosis: Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Brief history:
63 year-old male with multiple pulmonary nodules. Evaluate for metastases.
Images:
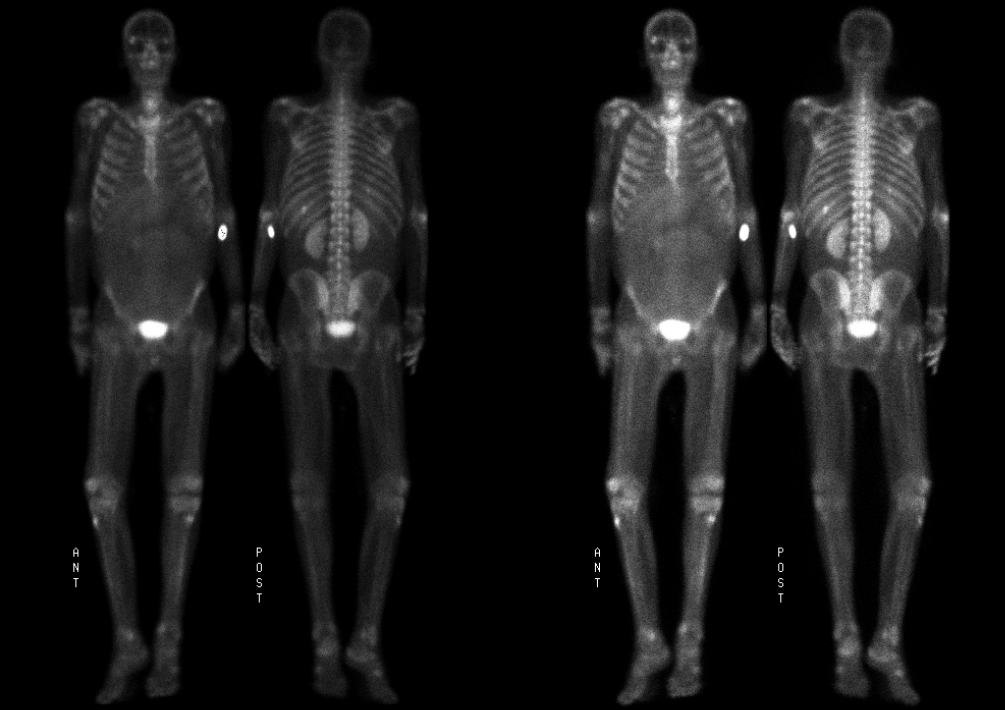
Anterior and Posterior Whole Body Scintigrams
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(ct).
Recent CT image.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Full history:
63 year old male with alcoholic cirrhosis who is found to have a hepatic mass, satellite lesions in the liver, and multiple pulmonary nodules on CT. Bone scan is performed to evaluate for osseous metastses.
Radiopharmaceutical:
20.2 mCi Tc-99m MDP i.v.
Findings:
Anterior and posterior delayed whole body scintigrams demonstrate a focus of increased radiotracer accumulation in the posterior aspect of the left eleventh rib. This focus was not explained on a CT of the chest and could represent a fracture or a metastases. There is mild diffuse activity throughout the abdomen and pelvis consistent with ascites. Also note the decreased visualization of the kidneys, lumbar spine, and sacrum on the anterior view due to the water density of ascites attenuating the photons from those structures. In the region of the left lobe of the liver there is activity associated with the patient's know hepatic tumor.
CT image of the abdomen demonstrates a mass in the left lobe of the small, cirrhotic liver and ascites.
Discussion:
Fluid collections such as ascites and pleural effusion can retain radiotracer on bone scintigraphy.
Causes of focal hepatic uptake of Tc-99m MDP include hepatoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastasis. Common metastases include those from colon, breast, ovarian, and lung carcinomas as well as melanoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Followup:
This patient with alcoholic cirrhosis, hepatic tumor, and pulmonary metastases was deteriorating. His tumor was presumed to be hepatocellular carcinoma (alpha-fetoprotein elevated at 95.2 ng/ml) but biopsy was not performed. He was discharged home and placed on hospice.
Major teaching point(s):
Always evaluate the soft tissues on bone scintigraphy.
Uptake in fluid collections, such as ascites or pleural effusion, does not indicate malignancy. After injection of the radiopharmaceutical, some of the tracer diffuses into the extracellular fluid space and, when that space is large, the tracer will not be cleared completely at the time of imaging.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Gasterointestinal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs146
Copyright by Wash U MO

