Case Author(s): Rusty Roberts, M.D. and Keith Fischer, M.D. , 10/11/04 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Breast cancer with subclavian obstruction
Brief history:
64 y/o woman with palpable right axillary masses and new shortness of breath
Images:
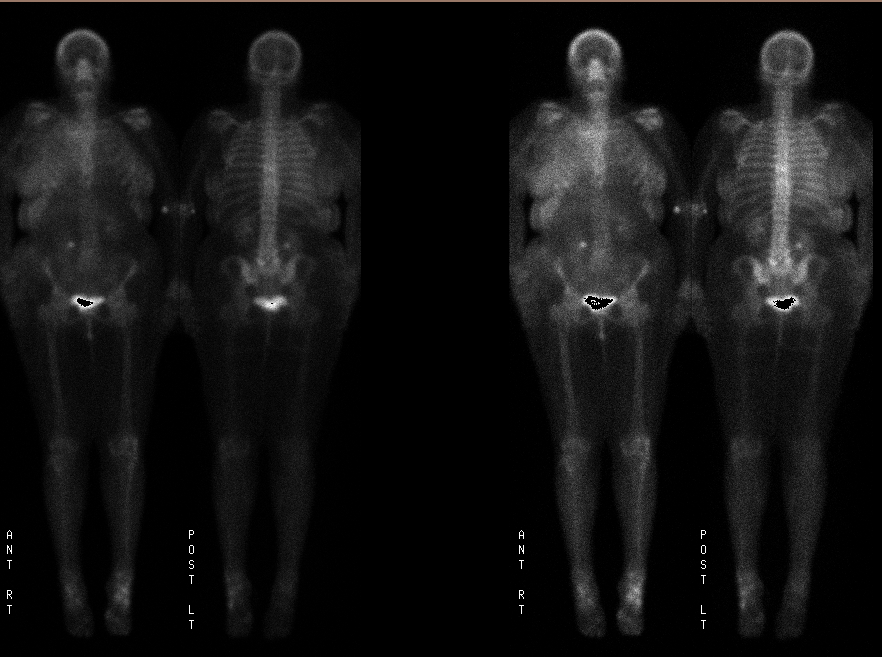
Dual intensity anterior and posterior whole body images
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
Spot images from bone scintigraphy
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Breast cancer with subclavian obstruction
Full history:
64 y/o woman with palpable right axillary mass on self exam presented to be evaluated for metastatic breast cancer. She had no other previous imaging exams at the time of presentation. She also complained of new shortness of breath. She has a history of cervical cancer.
Radiopharmaceutical:
21.7 mCi Tc-99m MDP i.v.
Findings:
Delayed whole-body scintigrams were obtained. There is diffuse soft tissue radionuclide deposition involving the right breast, chest wall and right lateral body wall to the level of the pelvis. On the posterior images diffuse activity is also seen overlying the right hemi-thorax.
Degenerative changes are seen at the L5-S1 facets. Degenerative changes are also seen within the ankles with the left being more prominent than the right.
Discussion:
Unilateral soft tissue deposition of MDP may be caused by unilateral vascular obstruction. Bilateral extremity tissue uptake is seen in vascular obstruction such as superior or inferior vena cava syndrome. Soft tissue uptake in general can be secondary to soft tissue deposition of calcium and can be seen in renal compromise. In this case the soft tissue deposition was secondary to subclavian vein obstruction. The increased posterior right thorax activity is from a malignant pleural effusion. Normal breast tissue may also take up MDP but not this diffusely and it would likely be symmetrical. In this case, lymphatic obsstruction in the right breast from tumor accounts for the marked uptake in breast.
Followup:
The new shortness of breath and physical exam at the time of the outpatient scintigram led a chest xray and CT after the radiopharmiceutical injection but prior to scintigraphy. She then returned for imaging at 2 hours. The CT images demonstrate patency of the superior vena cava but obstruction or compression of the subclavian vein. Large pleural effusion is also present. Axillary mets from an enhancing breast mass is seen.
Differential Diagnosis List
Diffuse soft tissue activity on bone scintigraphy can be caused by tumoral infiltration, vascular obstruction, lymph obstruction, thermal injury, frost bite, or trauma. Diffuse calcium deposition should also be considered.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs145
Copyright by Wash U MO

