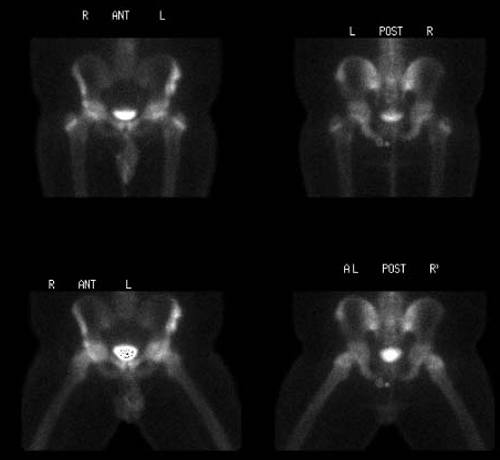

Static 2 hour post injection anterior and posterior images
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(xr). AP view of the pelvis
View third image(xr). Frog-leg view of the pelvis
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
AP and Frog-leg pelvis: A calcific density, that projects lateral to the left iliac crest, likely represents an avulsion of the left anterior superior and inferior iliac spines. Incidentally noted is a round calcific density projecting superior to the left iliac crest that may present a button on the patient or an enterolith. The hips are normal.
Avulsion fractures are common in the skeletally immature. Avulsion fractures result when abnormal stress is applied resulting in disruption at the weakest link - the apophyseal plate.
Anterior superior iliac spine avulsion fractures result from abnormal stress to the origin of the sartorius muscle. This occurs when the hip is extended and the knee flexed such as in jumping sports including basketball or volleyball. Anterior inferior iliac spine avulsion fracture results from abnormal stress to the origin of the rectus femoris muscle. This occurs with contraction of the rectus femoris muscle from vigorous kicking, such as in soccer.
Playing hacky sack requires a combination of jumping and kicking of a soft bean bag. Thus, it is not an unusual cause for these types of avulsion fractures.
Additional common sites of stress fracture in the pelvis include the lesser trochanter (insertion of the iliopsoas muscle) and the ischial tuberosity (origin of the hamstrings).
Normally about 80% of bone scintigraphy examinatinos demonstrate increased uptake at the site of fracture by 24 hours; about 95%, by 72 hours. In elderly or debiliated patients, increased uptake may not be demonstrated for several days. Gradual decline in activity occurs with time. About 65% of exams normalize by 1 year; 90%, by 2 years. The minimum time for normalization of activity is 6 months. Persistent activity can occur if healing has not resulted in anatomic alignment resulting in abnormal biomechanical stress and remodeling.
For companion case, see case bs076
REFERENCES: Browning KH. “Hip and Pelvis Injuries in Runners." The Physician and Sportsmedicine. Vol 29. 2001. Downloaded 1/31/04 from http://www.physsportsmed.com/issues/2001/01_01/browning.htm
Williams, SC (2001) Nuclear Medicine Online Reference Text. Bone Imaging: Trauma. Retrieved March 8, 2004, from Aunt Minnie Web Site: http://www.auntminnie.com/
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Effect of Trauma)
Return to the Teaching File home page.