Case Author(s): Bart Rydzewski M.D., Ph.D. and Henry D. Royal M.D. , 8/23/00 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Arterial injection of radiopharmaceutical.
Brief history:
58-year-old woman with a 10-week history of left hip and lower back pain
Images:
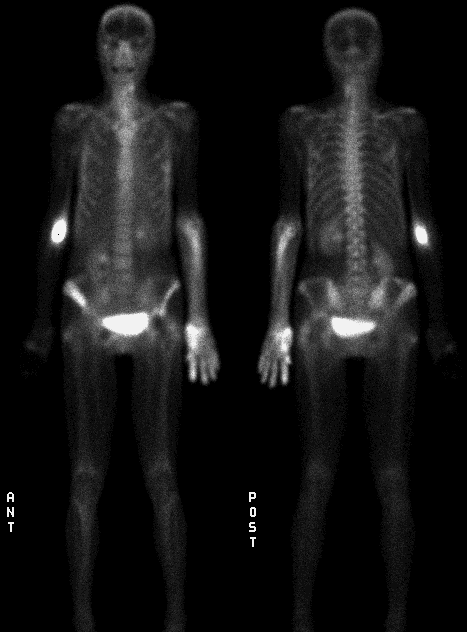
Dealyed anterior and posterior whole body images.
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
Delayed spot images.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Arterial injection of radiopharmaceutical.
Full history:
58-year-old woman who reports a 10-week history of left hip and lower back pain while walking and sitting. The patient has a total left hip arthroplasty and old fractures of the right superior and inferior pubic rami. Patient denies recent trauma or recent surgery.
Radiopharmaceutical:
20.9 mCi Tc-99m MDP i.v.
Findings:
There is diffusely increased activity in the distal left upper extremity extending from the level of the antecubital fossa to the tips of the fingers. This pattern is most consistent with an inadvertent arterial injection of radiotracer. The large focus of activity in the right antecubital fossa is due to extravasation of the radiopharmaceutical at this site.
There is a small area of mildly increased radiotracer in the right greater trochanter, which is probably secondary to enthesopathy. There is also a moderate amount of increased uptake in the right iliac bone, compatible with radiographic findings from 7-6-00 of old fracture. There is no activity in the right inferior pubic ramus where there is radiographic evidence for an old fracture. The superior pubic ramus can not be evaluated due to underlying bladder activity. There is mildly increased activity in left lateral ribs 6-9.
Discussion:
The presence of abnormal activity in the soft tissues on a bone scintigraphy study can be related to multiple factors and conditions. Generally, increased deposition of Tc99m-MDP is related to increased blood flow, soft tissue calcification, necrosis, neoplasm or inflammatory process. More diffusely increased soft tissue uptake is often related to metabolic conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, scleroderma, polymyositis, amyloidosis etc. Faulty preparation of tracer can also result in Tc-99m pertechnetate being deposited in thyroid gland, gut, salivary gland.
In this patient, the focal pattern of increased soft tissue uptake is consistent with inadvertent intraarterial delivery of the tracer. Intraarterial injection results in the delivery of a high concentration of the radiotracer to the soft tissues distal to the site of injection resulting in the classic findings presented here. Occasionally, extravasation of radiopharmaceutical at the site of injection can result in accumulation of activity within the lymph nodes.
References:
Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine Ed. MP Sandler, RE Coleman, FJT Wackers, JA Patton, A Gottschalk, PB Hoffer 1988 Williams&Wilkins 3rd edition
Followup:
The arterial injection of Tc-99m MDP was confirmed by the technologist who reported considerable difficulty in obtaining a venous access in this patient. A focus of increased activity in the right upper extremity is related to prior attempts of the radiotracer injection.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Vascular and Lymphatic Systems, Category:Other(Artifact))
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs121
Copyright by Wash U MO

