Case Author(s): Marc Montella, MD and Jerold Wallis, MD , 6/22/00 . Rating: #D3, #Q4
Diagnosis: Osteomalacia secondary to Fanconi's Syndrome
Brief history:
21 year old female with bone pain
Images:
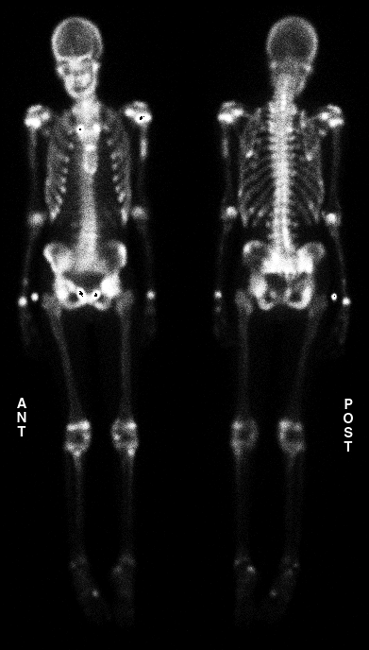
Whole Body Bone Scan
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
Spot Images from Bone Scan
View third image(xr).
Plain Film Right Shoulder
View fourth image(xr).
Plain Film Left Humerus
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Osteomalacia secondary to Fanconi's Syndrome
Full history:
21 year old woman with Fanconi's syndrome and known osteomalacia.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Tc-99m MDP
Findings:
Delayed whole-body scintigrams were obtained. There are multiple areas of abnormal uptake, many of which correspond with the patient's known fractures seen on the recent skeletal survey. Specifically, there is increased uptake within the superior pubic rami bilaterally adjacent to the pubic symphysis. In addition, there is minimal uptake seen within the inferior pubic rami, consistent with prior fracture. There is increased uptake seen in the left acetabulum (and to a lesser degree the right acetabulum), right sacroiliac joint region, left humeral shaft,multiple posterior and lateral ribs, right scapula and mid sternum.
Increased activity is seen in the physes diffusely, suggesting skeletal immaturity.
Radiographs of the shoulder demonstrate a line of decreased density in the scapula consistent with a Looser zone (poor calcification of callus in a incompletely healed stress fracture), which is seen in osteomalacia. These and other radiographs (not shown) demonstrate poor bony calcification, multiple healing insufficiency fractures, and bony resorption.
Discussion:
Fanconi syndrome is a generalized defect in proximal tubule transport involving amino acids, glucose, phosphate, uric acid, sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, and proteins. Idiopathic Fanconi syndrome may be inherited as an autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked trait.
Rickets and osteomalacia are common findings secondary to the hypophosphatemia.
Reference: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine
Chapter 276: Hereditary Tubular Disorders
Copyright 2001, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
John R. Asplin Fredric L. Coe
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Metabolic, endocrine, toxic)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs117
Copyright by Wash U MO

