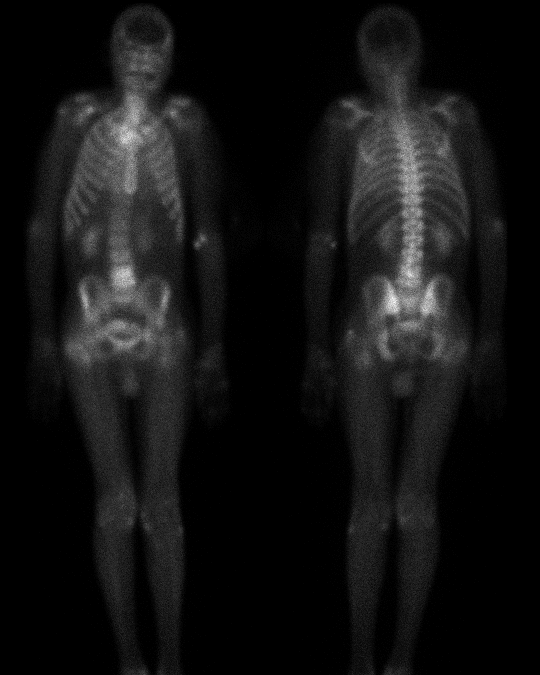

2-HOUR DELAYED ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR WHOLE-BODY IMAGES
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs). 24-HOUR DELAYED ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR PELVIC IMAGES
View third image(xr). LATERAL RADIOGRAPH OF THE LUMBAR SPINE
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
One month prior to this admission, the patient was admitted to the hospital with pneumonia and Klebsiella bacteremia. He was treated with intravenous antibiotics at that time and discharged.
Pertinent past medical history includes chronic renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, hepatitis B and C, and pyelonephritis.
On the 24-hour delayed images, the increased activity at L4-5 appears linear and horizontal, i.e., involving the disk space and adjacent vertebral body endplates. These findings suggest a disk-centered process, such as infection. Further scrutiny of the right femur reveals a linear band of increased activity extending across the intertrochanteric region, suggestive of fracture.
Radiographs of the lumbar spine show loss of disk height at L4-5 with adjacent vertebral body endplate destruction and sclerosis.
Radiographs of the right hip (not included) were suggestive, but not diagnostic, of a non-displaced intertrochanteric fracture.
MRI of the lumbar spine showed disk-space narrowing and bone marrow edema at the L4-5 level. The disk space enhanced at this level, and there was enhancement in the adjacent soft tissue extending posteriorly into the epidural space and anteriorly into the psoas muscle.
Aspiration of the L4-5 disk space showed a few neutrophils, but all bacterial, mycobacterial, and fungal cultures were negative. Despite the negative cultures, the combined radiological and scintigraphic findings are felt to be diagnostic of disk space infection.
MRI of the right hip showed a linear abnormal signal extending across the intertrochanteric region of the right femur, which was bright on STIR and dark on T1-weighted images. This correlates with the linear increased activity on bone scintigraphy, and is diagnostic of fracture.
View followup image(mr). MR IMAGES OF THE LUMBAR SPINE AND RIGHT HIP
Bone scintigraphy has a comparable sensitivity to MRI for detecting disk space infection.
SPECT and pinhole-collimator magnification images may be helpful for better defining the level of disk space infection and extent of involvement.
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Inflammation,Infection)
Return to the Teaching File home page.