Case Author(s): Sam Wang, M.D., and Jerold Wallis, M.D. , 6/10/97 . Rating: #D2, #Q4
Diagnosis: Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Brief history:
Woman with a lung mass.
Images:
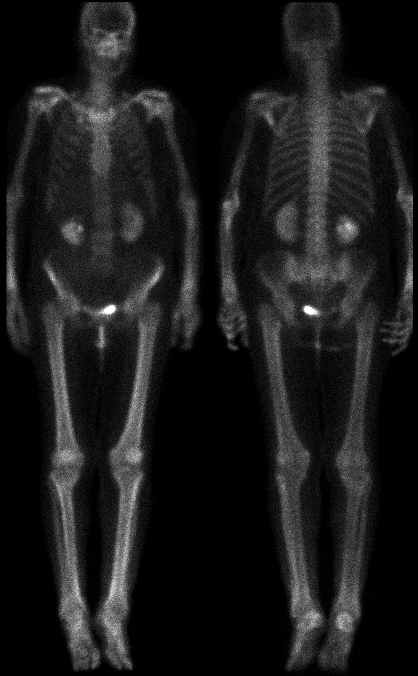
Anterior and posterior images
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
Full history:
Woman with a newly diagnosed posterior right upper lobe lung mass, being
evaluated for metastatic disease.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Tc-99m MDP
Findings:
Delayed whole body images
demonstrate linear cortical uptake of the
radiopharmaceutical in the lower extremities. The effect is also
seen to a lesser degree in the distal upper extremities.
Mild uptake at the right first rib costo-chondral junction is not
contiguous with the lung mass on chest CT (not shown). This is
a common site for degenerative change, and is relatively unlikely
to represent a solitary metastatic focus.
Discussion:
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy on
bone scintigraphy is generally characterized by
symmetric diffusely increased cortical uptake in the
metaphysis and diaphysis of the tubular bones of the
extremities. Pulmonary causes of
hypertrophic osteoarthropathy may include malignant
neoplasms (e.g., bronchogenic carcinoma,
a few benign
neoplasms (e.g., benign pleural fibroma), and chronic
inflammation (e.g., pulmonary abscess, cystic fibrosis,
interstitial fibrosis). Other causes of hypertrophic
osteoarthropathy include inflammatory bowel disease,
chronic liver disease, or congenital heart disease.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
- General ACR code: 48
- Skeletal System:
4.861 "Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy"
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Misc)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs077
Copyright by Wash U MO

