Case Author(s): Ed Grishaw, M.D. and Henry Royal, M.D. , 01/31/97 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Radiation nephritis
Brief history:
49-year old woman with
metastatic breast cancer
Images:
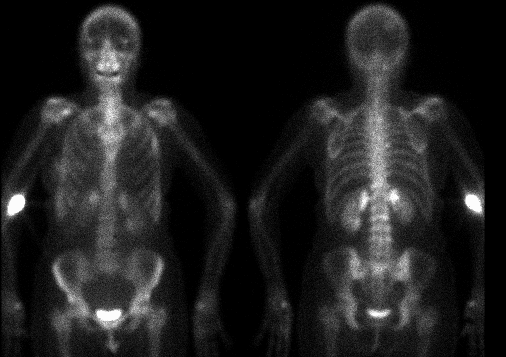
Anterior and posterior whole body images are shown. What is the
activity near the thoracolumbar junction?
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
For comparison, bone scintigraphy from 9 months earlier.
View third image(bs).
For comparison, bone scintigraphy from 6 months after the main image above.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Radiation nephritis
Full history:
49-year old woman with
breast cancer diagnosed in 1994, status post
left mastectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy.
The patient was subsequently discovered to
have osseous metastatic disease and received
radiation therapy to her thoracolumbar spine
in the fall of 1995.
Radiopharmaceutical:
21.0 mCi Tc-99m
MDP i.v.
Findings:
The bone scintigram dated 6-
17-96 demonstrates geometrically increased
uptake of radiopharmaceutical involving the
medial superior poles of the kidneys. Multiple
foci of abnormal radiopharmaceutical uptake
compatible with osseous metastatic disease
involve the left first rib anteriorly, the left
fourth rib laterally, the right parietal skull, as
well as the L2-L4 vertebral bodies. Compared
to the previous examination of 9-14-95, these
foci appear markedly less intense suggesting
interval improvement. The previously noted
metastatic foci involving T5-T7 on the study of
9-14-95 are no longer identified compatible
with interval healing.
Prior whole-body bone scintigrams dated 9-14-
95 and 1-30-97 have been included to
demonstrate interval appearance and
resolution of the geometrically increased
uptake involving the medial superior poles of
the kidneys. These finmdings are due to focal radiation nephritis caused by inclusion of the medial superior poles of
the kidneys in the
spinal radiation therapy port.
Discussion:
Clinically, the manifestations
of acute radiation nephritis present 6-12
months after treatment. Despite this term, the
condition is neither acute nor does it represent
nephritis. Pathologic correlation demonstrates
a nephrosclerosis. If diffuse and severe, the
patients typically present with anemia, edema,
hypertension, proteinuria, uremia, oliguria, and
in some cases frank anuria. Deaths secondary
to acute radiation nephritis are typically
secondary to malignant hypertension. Some
patients also develop body cavity effusions,
headaches, nausea and vomiting, and
occasionally photophobia, which often are
confused with recurrent tumor or the
development of distant metastases. In general,
renal radiation damage occurs with doses
greater than 2300 cGy over a 5-week period.
Renal injury is greater if there is concomitant
chemotherapy. With the performance of a
radionuclide bone scintigraphic study after
radiation therapy, increased uptake is
identified in the regions included within the
radiation port, typically between 6 months and
2 years after treatment. The reason for this
reversible abnormal radiopharmaceutical uptake is
transient renal dysfunction.
Chronic radiation nephritis typically develops
1-5 years after radiation therapy with a mean
time of approximately 2-3 years. Changes are
irreversible and progressive and treatment at
this point is usually symptomatic.
Pathologically, the findings within the chronic
clinical period demonstrate further progression
of the processes that developed in the subacute
clinical period. These findings include
progressive nephrosclerosis, fibrointimal
proliferation resulting in occlusion of the fine
vasculature, glomerulosclerosis, tubular
atrophy, and finally interstitial fibrosis.
Referemces: Mettler FA Jr and
Upton AC. Medical effects of ionizing radiation,
2nd edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co,
1995:254-255
Followup:
None
Major teaching point(s):
See Discussion
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Inflammation,Infection)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs071
Copyright by Wash U MO

