Case Author(s): Brigid Gordon,MD and Henry Royal, MD , 10/21/96 . Rating: #D2, #Q4
Diagnosis: Soft tissue mass in the abdomen.
Brief history:
73 year old male with newly diagnosed prostate cancer (PSA=8.0).
Evaluate for metastatic disease.
Images:
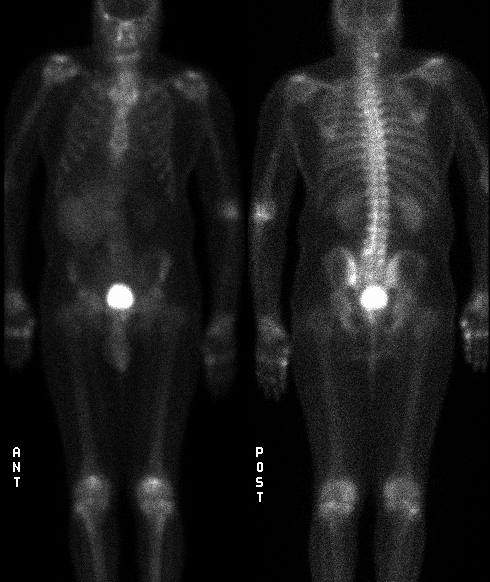
Anterior and posterior whole-body delayed images.
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
Oblique view of the chest and upper abdomen.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Soft tissue mass in the abdomen.
Full history:
73 year old male with newly diagnosed prostate cancer (PSA=8.0).
Evaluate for metastatic disease.
Radiopharmaceutical:
20.6 mCi Tc-99m MDP i.v.
Findings:
Large focus of increased tracer activity in the right upper quadrant. It
obscures the right kidney on the anterior view, but not on the posterior
view. No evidence of bony metastatic disease.
Discussion:
Normally, uptake of a bone scanning agent is seen in the osseous
structures, kidneys, and bladder. Occasionally, abnormal extraskeletal uptake in
soft tissue can be seen on delayed images. The pathogenesis of uptake in the soft
tissue is multifactorial. However, one of the primary underlying factors
responsible for the abnormal localization of bone scanning agents is excess
calcium in the soft tissue. For example, cell hypoxia and death lead to loss
of intracellular calcium and phosphate to the extracellular compartment
where precipitation as a calicium salt and binding to a bone agent can occur.
The uptake of the Tc-99m MDP is believed due to chemiabsorption.
Followup:
CT study of the abdomen and pelvis performed later on the same day as
the bone scintigraphy study. It identified a large, heterogeneously
enhancing mass measuring 12 x 6 x 28 cm centered in the greater omentum and
abutting the rectus muscle sheath.
REFERENCE:
Nuclear Medicine. Henkin et al., editor. Mosby, 1996.
View followup image(ct).
Large, heterogeneously enhancing mass centered in the greater omentum and
abutting the rectus muscle. Differential includes leiomyocarcoma, desmoid
tumor and remotely, fat necrosis. Biopsy revealed an extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumor. It was subsequently resected.
Major teaching point(s):
Soft tissue uptake of bone tracer.
Differential Diagnosis List
Leiomyosarcoma vs. desmoid tumor vs. fat necrosis.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Gasterointestinal System, Category:Neoplasm, Neoplastic-like condition)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs066
Copyright by Wash U MO

