Case Author(s): Mike Roarke, M.D, and Henry Royal, M.D. , 1/26/96 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Septic hip and surrounding myositis.
Brief history:
72-year old man with a history
of C3-5 laminectomy and pseudomeningocele, now
presents with history of fever and mental status
changes.
Images:
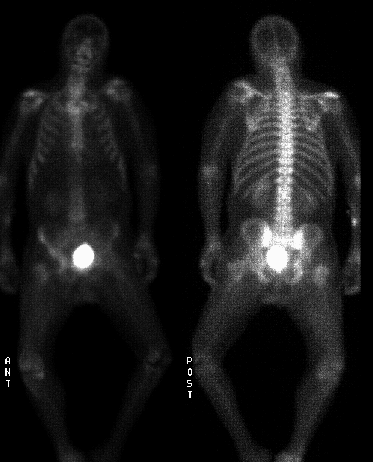
Whole body bone scintigraphy images.
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(ga).
Anterior image of the pelvis at 72 hours post injection.
View third image(ct).
Axial CT images.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Septic hip and surrounding myositis.
Full history:
72-year old male nursing home
patient with a history of cervical laminectomy in the
past requiring removal of hardware and debridement
four months ago. Now presents with new mental
status changes and fever. Whole body bone
scintigraphy was requested to exclude recurrent
osteomyelitis in the cervical spine.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Ga-67 citrate
Findings:
Whole body delayed bone
scintigraphy was performed. There is decreased
activity in the cervical spine on the posterior view,
corresponding to the prior laminectomy. No evidence
of osteomyelitis is seen in this area. However, there is
an area of decreased activity in the region of the right
femoral neck and head with correspondingly increased
activity in the acetabulum. Gallium scintigraphy
obtained 72 hours post injection reveals increased
activity in the soft tissues about the right hip joint.
Computed tomography confirms enlarged edematous
right hip musculature with only a small fluid
collection in the region of the gluteus maximus
muscle. Other than joint space narrowing, the right
femoral head is symmetric in appearance with the
left.
Discussion:
Gallium scintigraphy is often
used to improve the specificity for the detection of
osteomyelitis when focal areas of increased activity
are seen on bone scintigraphy. In this case, gallium
scintigraphy was useful in demonstrating that the
majority of abnormal tracer accumulation occurred
within the soft tissues surrounding the right hip.
These findings were concordant with the finding of no
significant abnormal soft tissue fluid collections in the
surrounding musculature on computed tomography
examination. While decreased Tc-99m MDP
accumulation in the femoral head and neck can be
seen in children with hip joint effusions, it is unusual
for septic arthritis to produce decreased activity in the
femoral head in an adult.
Followup:
Aspiration of the right hip revealed
staph aureus. The patient was not considered a
surgical candidate and therefore was treated
conservatively with intravenous antibiotics for six
weeks. Follow-up plain radiographs of the right hip
were not obtained as of this writing to determine
whether or not avascular necrosis of the femoral head
had occurred.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Inflammation,Infection)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs051
Copyright by Wash U MO

