Case Author(s): Charles Pringle, M.D./ Tom R. Miller M.D., Ph.D. , 08/17/95 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Discitis with osteomyelitis
Brief history:
63-year old woman with one-
month history of lower back pain.
Images:
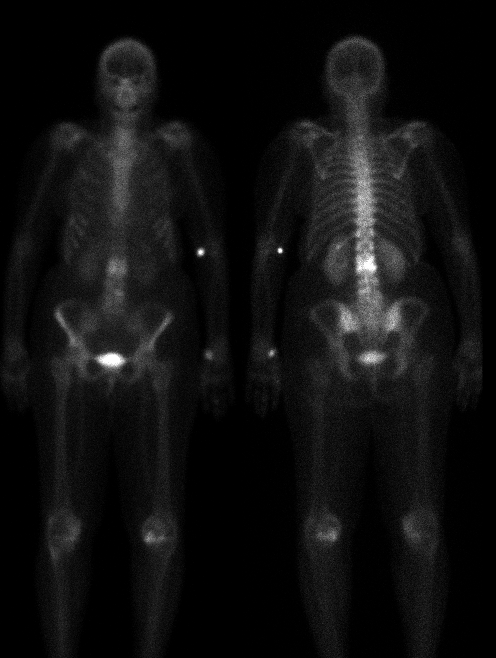
Anterior and posterior whole body delayed
images
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(mr).
Sagittal unenhanced and enhanced M.R.I. of the lumbar spine
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Discitis with osteomyelitis
Full history:
63-year old woman with sudden
onset of lower back pain approximately one month ago
after playing golf. The pain has continued to increase
in severity. Previous lumbar spine radiographs were
normal except for degenerative change.
Radiopharmaceutical:
20.2 mCi Tc-99m MDP
i.v.
Findings:
Delayed whole body images show
focal, intensely increased uptake at L2-3. Plain
radiographs demonstrate demineralization and
destruction of the anterior aspect of the L2 inferior
endplate and L3 superior endplate with probable
decrease in disc space at this level.
Discussion:
Discitis in the adult is generally
due to blood-born bacterial invasion of the disc from
adjacent endplates via communicating vessels. The
most common bacterial agent is Staphylococcus
aureus, gram-negative rods in intravenous drug
abusers, and, increasingly, tuberculosis. As in this
cases, the plain films are often negative early in the
course of the process. Later, there is destruction of
adjacent endplates, finally with endplate sclerosis
during healing. Bone scintigraphy is a sensitive
method for evaluating possible discitis.
Followup:
An MRI examination of the
lumbosacral spine was performed on the same day as
the bone scintigraphy. On T1 weighted images, there
is low signal in the adjacent areas of the L2 and L3
vertebral bodies and the L2-L3 disc space. These same
areas enhance after gadolinium administration.
There is also increased signal in the same area on T2-
weighted images. Additionally, there is a small
epidural inflammatory mass at the L2-L3 level, which
is anterior to the spinal cord. The MRI findings were
consistent with L2-L3 discitis and adjacent
osteomyelitis. The next day, the patient underwent a
fluoroscopically guided disc-space biopsy at the L2-L3
level, which subsequently grew Streptococcus
viridans. The patient was treated with intravenous
antibiotics.
Major teaching point(s):
The increased activity
involving two adjacent vertebral bodies on bone
scintigraphy is highly suggestive of discitis.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Spine and Contents, Category:Inflammation,Infection)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs032
Copyright by Wash U MO

