Case Author(s): M.C.Roarke, M.D., and Keith Fischer, M.D. , 8/7/95 . Rating: #D2, #Q3
Diagnosis: Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Brief history:
74-year old woman with chronic
left ankle pain and no known history of trauma.
Images:
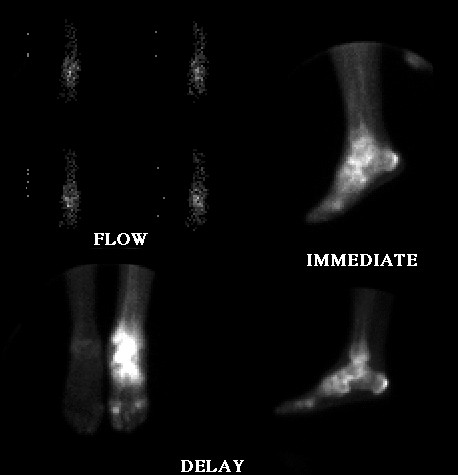
Flow images of both ankles, immediate static image of the left ankle and delayed images of the left ankle are shown
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(xr).
Plain radiograph of the left foot and ankle.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Full history:
74-year old woman with chronic
left ankle pain and no known history of trauma.
Radiopharmaceutical:
21.2 Tc-99m MDP i.v.
Findings:
Bone scintigraphy shows increased
activity on radionuclide angiogram, blood pool, and
delayed images throughout the left ankle and foot.
The accompanying radiographs dated 6-15-95 reveal
marked swelling of the soft tissues of the left foot and
ankle as well as diffuse osteopenia. The combined
scintigraphic and radiographic findings as well as the
clinical history permit a diagnosis of reflex
sympathetic dystrophy.
Discussion:
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy,
also known as Sudeckšs atrophy and causalgia, is a
sympathetic mediated disorder of the extremities
characterized by pain, stiffness, swelling, weakness,
and skin changes, and vasomotor instability.
Radiographically, soft tissue swelling and osteopenia
are seen. Scintigraphically, there is increased activity
in the affected limb during the radionuclide
angiographic and immediate post injection images.
Delayed scintigraphy reveals increased activity,
diffusely in the hand foot. Treatment strategies
include physical therapy and, in refractory cases,
neurosurgically created dorsal root entry zone lesion.
References: Resnick. Diagnosis of
Bone and Joint Disorders, 2nd edition, 2037-2043.
Differential Diagnosis List
Differential
considerations include an infectious etiology such as
osteomyelitis, although the diffuse pattern of uptake
argues against this. Arthritides such as rheumatoid
arthritis and the rheumatoid variants would be
expected to be more joint centered. Frostbite or
electrical injury might also be considered, but the
predominance of proximal foot and ankle involvement
rather than distal involvement makes these
possibilities less likely.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Effect of Trauma)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs031
Copyright by Wash U MO

