Case Author(s): Hamid Latifi, MD, Tom R. Miller, MD, PhD , 11/8/94 . Rating: #D2, #Q4
Diagnosis: Bone infarct in a patient with sickle cell disease.
Brief history:
20 year-old man with left chest pain and sickle cell disease.
Images:
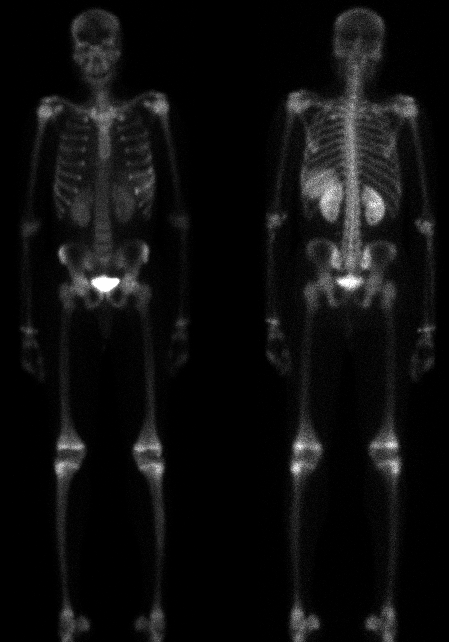
Anterior and posterior whole-body bone scintigraphy.
View main image(bs) in a separate image viewer
View second image(bs).
Oblique views of the ribs.
Full history/Diagnosis is available below
Diagnosis: Bone infarct in a patient with sickle cell disease.
Full history:
The patient is a 20 year-old man with sickle cell disease who was admitted with sickle crisis and left chest pain.
Radiopharmaceutical:
Tc-99m MDP
Findings:
Diffuse mildly increased tracer uptake is seen in the left 6th and 7th ribs.
Splenic uptake is noted consistent with splenic infarctions. The kidneys are enlarged.
Increased tracer accumulation in a periarticular distribution is also seen, which is
due to marrow expansion in response to the patient's anemia.
Discussion:
The increased splenic uptake is due to infarction (autosplenectomy).
Soft-tissue uptake in infarction is caused by migration of calcium into the infarcted tissue with the Tc-MDP following the calcium. Frank, radiographically evident
calcification will not necessarily be present. Nephromegaly commonly accompanies sickle cell disease.
The increased rib uptake may be due to bone infarction, osteomyleitis or trauma.
Followup:
The patient was treated conservatively for his symptoms, and subsequently improved.
Major teaching point(s):
The combination of splenic uptake and nephromegaly is almost pathognomonic of sickle cell disease.
Focal bone uptake in such patients is usually due to infarction or osteomyelitis.
ACR Codes and Keywords:
References and General Discussion of Bone Scintigraphy (Anatomic field:Skeletal System, Category:Other generalized systemic disorder)
Search for similar cases.
Edit this case
Add comments about this case
Read comments about this case
Return to the Teaching File home page.
Case number: bs013
Copyright by Wash U MO

